- Understand the scope: .wslconfig is global (WSL 2) and wsl.conf is per distribution.
- Properly restart WSL (8-second rule) to apply changes.
- Optimizes resources and I/O: memory, swap, filesystem Linux and DrvFs.
- Strengthen security and management with Intune, GPO, and appropriate network modes.
If you're working with Linux inside Windows, the key to maximizing performance and stability lies in two configuration files: .wslconfig and wsl.confWith these settings, you can adjust everything from how much memory the WSL 2 VM uses to how drives are mounted, which DNS servers are used, or whether systemd is enabled in your distribution. Here you'll find a Guide to creating environments with WSL2 and Docker, practical and detailed to master these options without complicating your life.
Before getting started, it's important to be clear on two ideas: .wslconfig applies global WSL settings (WSL 2 only) y wsl.conf defines the behavior for each distributionFurthermore, there's an unwritten rule: whenever you change something, you must properly restart WSL for the changes to take effect. From here, we'll get down to business with everything you need to know and do, using real-world examples. commands and good practices.
Key differences between .wslconfig and wsl.conf
There is a very clear boundary between the two files: .wslconfig is global and exists outside of Linux (on Windows), while wsl.conf is local to each distro and it's stored within the Linux system itself. Understanding this saves you headaches when debugging problems.
In summary: .wslconfig is located in %UserProfile%\\.wslconfig (It doesn't exist by default; you have to create it) and controls the WSL 2 VM (memory, CPU, kernel, networking, etc.). For its part, wsl.conf is located in /etc/wsl.conf within the distribution and governs auto-assemblies, internal network options, interoperability with Windows, default user, Boot and more.
Important: The .wslconfig options only affect WSL 2If you have a distro running WSL 1, these global options will not apply.
The “8-second rule” and how to properly restart WSL
When you change any parameter in .wslconfig or wsl.confIt is not enough to simply close the window of the terminalYou must wait for the WSL VM to stop completely, which usually takes about 8 seconds after closing all sessions.
If you want to force a clean reboot, see the commands to restart WSL and use PowerShell with these commands: wsl --list --running (to check which distros are still active) and wsl --shutdown (to shut them all down). You can also terminate a specific distribution with wsl --terminate <NombreDistro>This step is vital for the changes are applied correctly.
wsl.conf: configuration by distribution (WSL 1 and WSL 2)
The file /etc/wsl.conf It allows you to adjust behavior at the distribution level. It supports INI-type sections: , , , , plus , y In recent systems, it's perfect for deciding how drives are mounted, whether to add the Windows PATH, or which user is used by default.
You can open it with your favorite editor like root: sudo nano /etc/wsl.confIf it doesn't exist, create it. After editing, remember to apply the WSL shutdown rule so that changes take effect.
Enable systemd on your distro
WSL incorporates support for systemd in recent versions (WSL 0.67.6 or higher). If your workflow requires it (for example, services that start via systemd), you can enable it with two lines in wsl.conf:
systemd=true
Check your version with wsl --version and, after editing, run wsl.exe --shutdownTo verify, use systemctl list-unit-files --type=service and you'll see the status of the services. This feature brings WSL closer to a true Linux experience. If you need more in-depth management information, see how manage services with systemd to see practical examples.
Windows Drive Automount (DrvFs)
This section defines how drives like C: or D: are mounted within Linux using DrvFs. You can enable or disable it, change its root, or add permission options.
- enabled (boolean): By default true, mounts C:/ or D:/ under
/mnt. - mountFsTab (boolean): by default true, causes WSL to process
/etc/fstabat the beginning. - root (string): by default
/mnt/You can change it to/windir/and you'll see/windir/c. - options: DrvFs-specific comma-separated list (permissions and metadata).
Useful DrvFs options: uid, gid, umask, fmask, dmask, metadata and case. If you activate metadataYou can use masks like umask=022 o dmask=000 and fine-tune permissions as you would in "pure" Linux. If your workflow requires Access Linux partitions from WindowsThis section and DrvFs are key to adjusting permissions and assembly.
What exactly is DrvFs?
DrvFs is the file system bridge between Windows and Linux in WSL. It allows you to mount Windows drives in /mnt/c, /mnt/detc., and define how permissions, case sensitivity, and metadata are managed. If you need more Linux-like behavior, active metadata and adjust permission masks to your liking.
Network, interoperability, default user, and boot
You can control the hostname, and whether WSL autogenerates it. /etc/hosts y /etc/resolv.confAdjusting this is useful if you prefer to manage DNS manually to achieve more stable or faster resolutions.
This section defines whether you can launch Windows processes from Linux (for example, notepad.exe) and if the Windows PATH is added to $PATHIf you're looking for a more "isolated" Linux environment, disable these options to avoid interference.
Here you choose the default user that the distro boots as. It's best to set it to your normal user account and not root for security reasons, although you can always log in as root occasionally. wsl -u root.
With this you can trigger a command when WSL starts (for example, service docker startand protect the automatic generation of binfmt if you have systemd. It's a practical way to automate services at startup.
GPU and time synchronization
The section lets you decide if the apps Linux can access the Windows GPU through paravirtualization. By default, it comes enabled=true, ideal for workloads of IA or graphics.
You can make WSL use and synchronize the Windows time zone with useWindowsTimezone=trueIt's a simple aid for avoid discrepancies and imbalances when changing time zones or putting the computer to sleep. If your goal is to use the GPU for computing, check how Install CUDA on WSL and leaves the drivers and updated toolkits.
Complete example of wsl.conf
This example shows several useful options: root change of assembliesDrvFs permissions, Own DNS and default user. Note: Remember to restart WSL to see the effects. If you set up a development environment, you can follow these steps to Configure a development environment with WSL that integrate these options.
# /etc/wsl.conf
enabled=true
root=/
options="metadata,uid=1003,gid=1003,umask=077,fmask=011,case=off"
mountFsTab=true
hostname=DemoHost
generateHosts=false
generateResolvConf=false
enabled=false
appendWindowsPath=false
default=DemoUser
command=service docker start
.wslconfig: WSL 2 VM global settings
This is where you decide how much memory, CPUs, or swap the VM will have, whether you use a custom kernel, and how the network behaves. Create the file in %UserProfile%\\.wslconfigTo open the folder from PowerShell, use cd ~ or type the path directly into the Explorer with % UserProfile%.
Key parameters in the section:
- kernel: absolute path in Windows to a custom Linux kernel.
- kernelModules: VHD with custom kernel modules.
- memory: RAM limit (default 50% of Windows RAM).
- processors: logical cores for the WSL 2 VM.
- localhostForwarding: exposes WSL ports in
localhost:puertoof the host. - kernelCommandLine: extra kernel parameters (e.g.,
vsyscall=emulate). - safeMode: safe mode to recover problematic distros (Windows 11).
- swap y swapFile: size and path of the swap disk.
- pageReporting: automatically returns unused memory to the host.
- guiApplications- Enables or disables WSLg (Linux GUI apps).
- debugConsole, maxCrashDumpCount: debugging and dump management.
- nestedVirtualization: nested on/off virtualization.
- vmIdleTimeout: milliseconds of inactivity before shutting down the VM.
- dnsProxy, networkingMode, firewall, dnsTunneling, autoProxyAdvanced network and proxy controls.
- defaultVhdSize: maximum size of the distro's VHD (e.g., 1 TB).
Formatting notes: entries of type path They must use Windows routes with double backslash, For example: C:\\Temp\\myCustomKernelSizes accept units (MB/GB); if you omit the unit, they are interpreted as bytes. Some options require Windows 11 and recent versions of WSL.
Networking: NAT, mirrored, virtio and more
With networkingMode You choose the network mode: NAT (default), mirrored, virtioproxy, bridged (obsolete) or noneIn NAT, WSL appears behind an internal NAT; in mirrored configuration, the network stack is reflected, simplifying access from the LAN to WSL services; with virtioProxy, an alternative backend is used. If you use mirrored, you can fine-tune with ignoredPorts to allow Linux to bind ports even if Windows uses them.
To expose services on your local network using mirroring, add to .wslconfig:
networkingMode=mirrored
Tras wsl --shutdownYou can adjust the Hyper-V firewall using PowerShell (administrator):
New-NetFirewallHyperVRule -DisplayName WSLPrivateInboundRule -Profiles Private -Direction Inbound -Action Allow -VMCreatorId ((Get-NetFirewallHyperVVMCreator).VMCreatorId)
# (Menos seguro) Desactivar la protección de Hyper-V por completo:
# Set-NetFirewallHyperVVMSetting -Name ((Get-NetFirewallHyperVVMCreator).VMCreatorId) -Enabled False
Keep the active firewall on public networks and limit exposure. If you need production, consider Reverse proxy and TLS.
experimental setup
This section allows you to activate features in preview. Among others: autoMemoryReclaim (disabled, gradual, dropCache), sparseVhd (scattered VHDs), bestEffortDnsParsing, dnsTunnelingIpAddress, initialAutoProxyTimeout, ignoredPorts y hostAddressLoopbackSome require Windows 11 22H2+ and are intended for optimize memory and network in specific scenarios.
Example of a commented .wslconfig
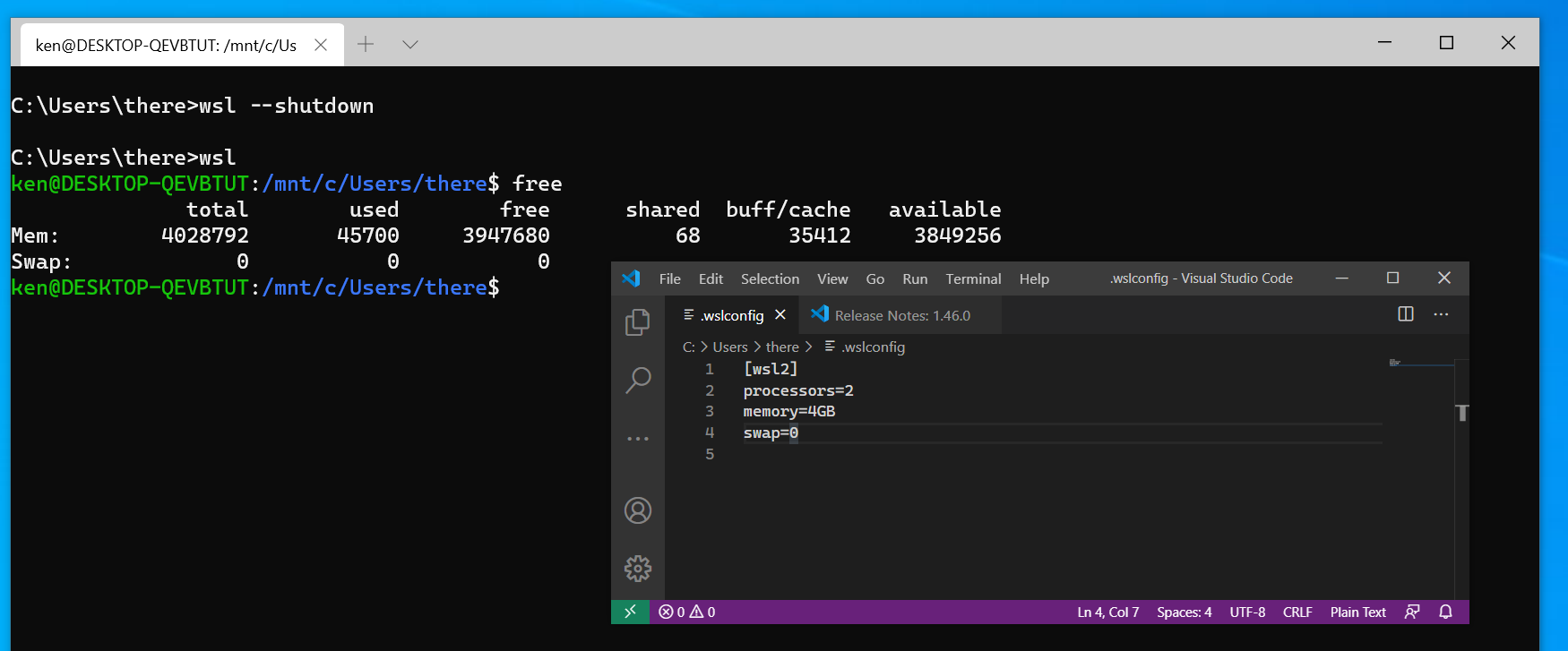
This example limits resources, uses a custom kernel, adjusts swap, and enables debugging features. Perfect for standardize environments in development teams.
# %UserProfile%\\.wslconfig
memory=4GB
processors=2
kernel=C:\\temp\\myCustomKernel
kernelModules=C:\\temp\\modules.vhdx
kernelCommandLine=vsyscall=emulate
swap=8GB
swapFile=C:\\temp\\wsl-swap.vhdx
pageReporting=false
localhostForwarding=true
nestedVirtualization=false
debugConsole=true
maxCrashDumpCount=10
sparseVhd=true
Optimize I/O and memory performance
For intensive work (for example, processing hundreds of 20 MP images (with ODM), it is advisable to adjust global resources and work in the native Linux file system to avoid I/O penalties on /mnt/cSet sufficient memory and swap limits in .wslconfig and check the actual usage with htop o free -h.
Practical recommendations: save your project in /home/Disable auto-mounts if you don't need them, and if the process still runs out of memory, swap increase (e.g., 16 GB) and allocated RAM (e.g., 8–12 GB depending on your machine). If you create .wslconfig If it's the first time and "it doesn't work," make sure it's in % UserProfile%, that the name is literal .wslconfig (without hidden extension) and of Restart WSL completely.
DNS and name resolution
By default, WSL uses the host's DNS servers, but you can choose not to auto-generate them. resolv.conf and put your servers (Cloudflare, Google, corporate) to achieve more predictable resolutions. In /etc/wsl.conf:
generateResolvConf=false
Then create or edit /etc/resolv.conf with the desired entries:
nameserver 1.1.1.1
nameserver 8.8.8.8
If you use modes like dnsProxy o dnsTunneling from .wslconfigAlso check its parameters and, if necessary, adjust dnsTunnelingIpAddress or active bestEffortDnsParsing to resolve requests ignoring unknown records.
Installation and first steps
WSL comes with Windows, but you have to enable it and install a distroIn modern builds (20262+), simply run from PowerShell or CMD: wsl --installThis command enables the WSL and VM Platform components, downloads the kernel, sets WSL 2 as the default, and installs Ubuntu (may require a reboot).
When you open the distro from Start for the first time, you will be prompted to create Linux username and passwordThey are independent of your Windows account, and that account will be the one that logs in by default. To change the password, use passwdIf you forget it, open the distro as root with wsl -u root o wsl -d <Distro> -u root and run passwd <usuario>.
Update packages and choose where to save your projects
Keep your packages up to date with sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade (Ubuntu/Debian). And remember this golden rule: Work in the FS where your tools are locatedIf you compile and run using Linux tools, save in \\wsl$\\<Distro>\\home\\<Usuario>If you use Windows tools, keep the files in C:\\Users\\<Usuario>.
To open the current WSL directory in Explorer, run explorer.exe .You can also navigate to routes like \\wsl$\\Debian\\home\\tu-usuario From Windows. If the folder appears empty, open a WSL terminal to activate the VM.
Windows Terminal and code editors
The experience is greatly improved with Windows Terminal (tabs, panels, GPU rendering, themes…). Each installed distro will appear as a configurable profile. For development, the most convenient option is usually… Visual Studio Code with the Remote Development Support (WSL) extension. From the distro, launch code . and you'll have a complete editing environment within WSL.
If you work in C++, Visual Studio 2022 integrates native support for CMake projects targeting WSL o SSH, allowing you to compile and debug on Linux from the same instance of VS.
Git, containers and databases
setup Git in WSL And, if you need it, the credential manager so you don't have to type passwords. Check line endings and files. .gitignore To avoid platform-specific issues, VS Code integrates Git commands that work seamlessly with WSL.
With DockerDesktop With WSL 2, you can use containers in an agile way and, if you're interested, connect your project to a remote development container. databasesWSL supports it without any problems MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB, Redis, SQL Server or SQLiteIt is an ideal environment for cross-platform local development.
GPU acceleration and graphics apps
WSL allows you to take advantage of the GPU of the team For heavy workloads (AI, CUDA, etc.). In practice, just make sure you have up-to-date drivers and toolkits and, if necessary, validate with containers like nvidia/cuda. Also with wslg you can run Linux GUI applications without setting up an external X server.
Useful interoperability commands
There is a very practical coexistence between both worlds. From Windows: wsl ls -la to list with Linux tools and filter with findstr or vice versa (mix dir y grepFrom Linux, launch any Windows app with .exe, for example notepad.exe .bashrc. You also have wslpath to translate routes between systems: wslpath RUTA_WINDOWS o wslpath -w RUTA_LINUX.
Mounting disks and working with external drives
If you need to access a physical disk or memory USB From WSL 2, you can set it up using wsl --mount and manage it as you would in Linux. Remember to check the file system and whether root permissions are required to avoid mounting errors.
Security and administration in the enterprise (Intune and GPO)
Now you can manage WSL with tools like Microsoft IntuneFrom the portal, create a configuration catalog profile and search for “Windows Subsystem for Linux” to see all available options. This is ideal for enforcing policies such as exclusive use of WSL Store, disable WSL 1 or prevent custom kernel and network configurations.
Recommendation for hardening in corporate environments: disable AllowInboxWSL (force Store version), AllowWSL1, the debug shellKernel/command-line configuration, custom networking, firewall via .wslconfig, nested virtualization, or kernel debugging. These GPOs are defined using the WSL ADMX, available on GitHub, and importable for local management.
Access control and commands
Policies AllowWSL, AllowInboxWSL y AllowWSL1 They control who can use WSL and which version. You can also allow or block users. wsl --debug-shell y wsl --mount according to your security requirements. It's an additional layer for avoid unwanted configurations in managed teams.
Troubleshooting: Creating .wslconfig and memory cases
If .wslconfig “does nothing”, verify that the file is in %UserProfile%\\.wslconfig, without hidden extension or strange BOM, and that its syntax is valid (section and key=value pairs). After creating or modifying it, run wsl --shutdown and open the distro.
For memory-intensive loads (such as batches of 470 20MP images), increases the allocated RAM and swap space. Example starting point:
memory=12GB
processors=8
swap=16GB
swapFile=C:\\WSL\\swap.vhdx
pageReporting=true
Also check that the project is in the Linux FSIf you continue to receive “out of memory” messages, check the tool's own limits (ODM parameters), and activate autoMemoryReclaim If you're interested in quickly recovering cache and monitoring usage, top/ htopDon't forget that Windows also needs sufficient free RAM.
Extra good practices and resources
When experimenting with network mirroring, adjust the firewall carefully; if You disable rules To test, reactivate them afterward. If you need additional documentation or alternative examples, you can explore external resources such as this PDFAnd if you're working with GPUs, validate your stack (drivers, CUDA/toolkit, versions) before getting started.
For those who manage fleets, the combo Intune + ADMX It gives fine control over what can be modified in .wslconfig, which commands are allowed, and whether WSL 1 distributions are accepted. This helps to standardize environments, reduce incidents and raise the level of security.
With these settings, you have a holistic guide to setting up WSL professionally: Use wsl.conf to profile each distro, .wslconfig to govern the global VMRestart WSL wisely, take advantage of Linux's native FS for performance, leverage GPUs and advanced networking, and if you work in a company, rely on policies to keep everything under control.
Passionate writer about the world of bytes and technology in general. I love sharing my knowledge through writing, and that's what I'll do on this blog, show you all the most interesting things about gadgets, software, hardware, tech trends, and more. My goal is to help you navigate the digital world in a simple and entertaining way.