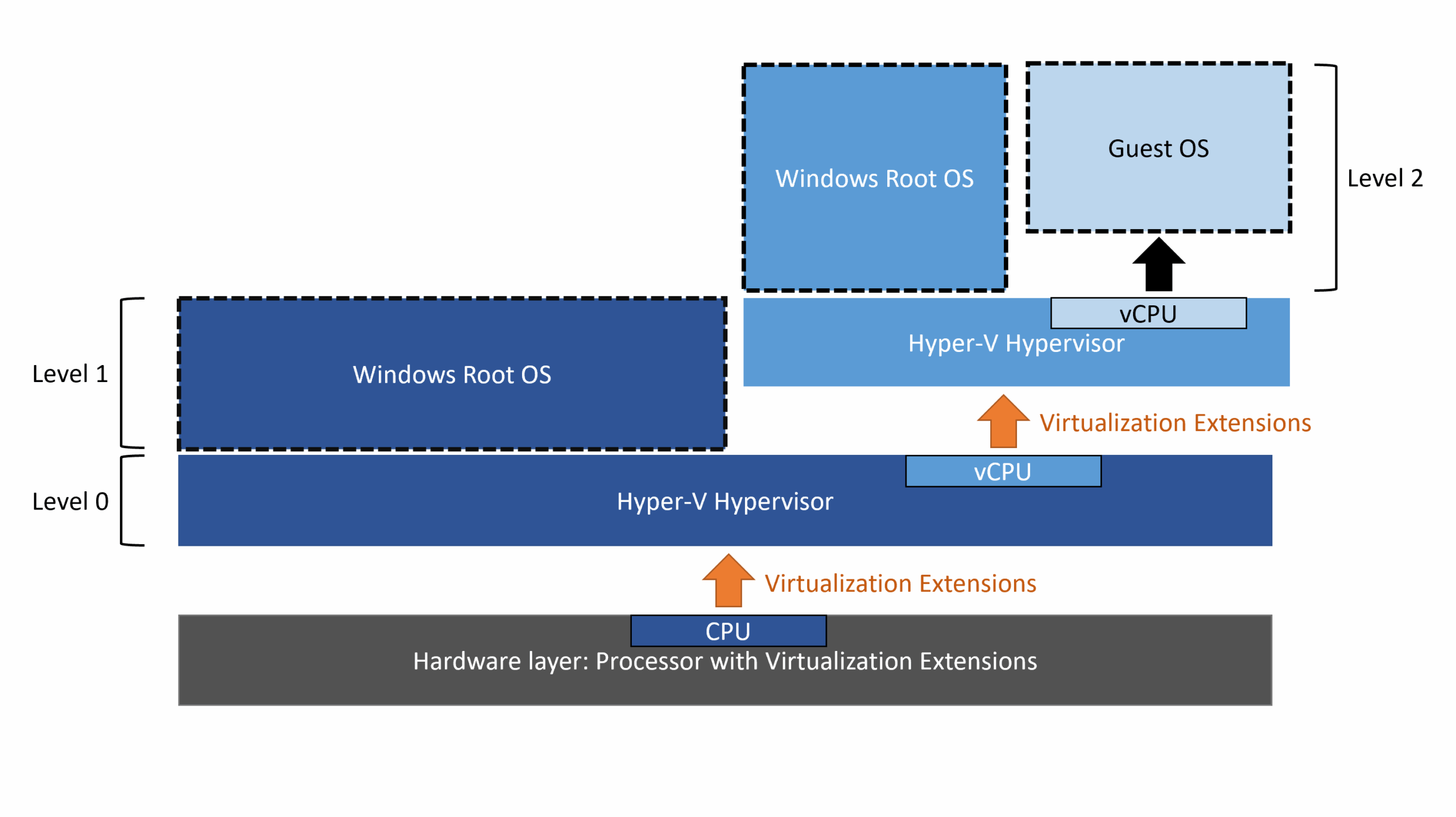
- Hyper-V, VirtualBox y VMware They offer different virtualization solutions according to needs, cost and compatibility.
- While Hyper-V excels in professional environments with WindowsVirtualBox triumphs due to its free nature and versatility, and VMware provides maximum power and advanced options.
- The appropriate choice depends on the operating system, user experience, and integration or graphics performance requirements.
Virtualization has become a fundamental tool for both home users and businesses, allowing multiple systems to run. OS on a single physical computer. Thanks to hypervisors, it is possible to set up test environments, software isolation, and even manage server infrastructures without the need to invest in hardware additional. In this analysis we are going to thoroughly squeeze the Differences between Hyper-V, VirtualBox, and VMware, reviewing everything from their strengths to their limitations, and resolving the most common doubts about which one to choose according to your needs.
With so many different solutions on the market, choosing the right one can be a real headache. That's why, here you'll find a comprehensive and natural breakdown, clearly explaining what distinguishes each option, what type of user will benefit most from it, and how their performance, compatibility, ease of use, advanced features, and much more compare. Let's find out everything.
What is a hypervisor? Types and basic operation
Before we get into the nitty-gritty, it's worth knowing what a hypervisor is. It's specialized software that allows you to run one or more Virtual machines, each with its own operating system, on a single physical hardware (the host). The hypervisor creates an abstraction layer between the hardware and the host software., making it easier for different environments to coexist safely and independently.
There are two main types of hypervisor:
- Type 1 (bare metal): It runs directly on the computer's hardware, without the need for a host operating system. It's ideal for professional and server environments, providing the best performance and security. Examples include Hyper-V in dedicated mode and VMware ESXi.
- Type 2 (hosted): It works like an additional application within an operating system. It's the most common choice for home users or developers who want to test systems and applications locally. Examples include VirtualBox, VMware Workstation/Fusion, and Hyper-V installed as an additional feature in Windows.
Hyper-V: Microsoft's professional bet

Hyper-V It is available in Pro, Education, or Enterprise editions of Windows 10 and 11, as well as Windows Server. It is a type 1 hypervisor, designed to run directly on the hardware, although it can also be installed on Windows as another component.
Its integration into the Windows ecosystem is one of its main advantages. It allows you to manage virtual machines through the Hyper-V Manager, PowerShell and Windows Admin Center, facilitating automation and centralized management in enterprises. Hyper-V excels in server, workstation, and platform deployments where security and isolation are key.
Among its advanced features are:
- Cluster support (high availability) y volumes of storage shared for business environments.
- Control points (checkpoints) standard and production, which allow you to roll back the state of a VM at any time.
- Integration services that improve performance and communication between host and guest.
- Live migration of virtual machines between hosts with virtually no downtime.
- Hardware-accelerated virtualization thanks to VT-x or AMD-V technology.
On the other hand, Hyper-V is only available for Windows and requires a Professional edition, leaving it out of reach for Windows Home users. Additionally, its use may seem less intuitive for those new to virtualization, and some non-Windows systems may present more difficulties during integration.
An interesting feature for advanced users is Windows Sandbox, which creates a temporary virtual environment for quick and safe testing, discarding all changes when you log out. It also integrates with WSL2 (Windows Subsystem for Linux) and platforms like Docker.
VirtualBox: The free and versatile solution
VirtualBox, owned by Oracle, is one of the most popular cross-platform alternatives being free, open source and compatible with Windows, Linux, macOS, Solaris and FreeBSD.
Its strength lies in the great compatibility on both host and guest operating systemsYou can install everything from older versions of Windows and Linux to less common systems like DOS, BSD, and even macOS (with certain Tricks additional). In addition, it stands out for offering:
- Easy setup and quick start-up, ideal for those starting out in virtualization.
- Snapshots to save and restore the state of VMs in seconds.
- Guest Additions To improve performance, enable shared folders and clipboard bidirectional.
- Software virtualization: Supports older hardware without VT-x or AMD-V extensions, although at a slower speed.
- Flexible network modes: NAT, bridge, internal, host-only, etc.
Despite being very complete, VirtualBox has some limitations compared to commercial rivals:
- Lower performance compared to VMware, especially on demanding machines.
- Limited support for 3D graphics (max. DirectX 9/OpenGL 3.0 and 128 MB VRAM per VM).
- Some useful extensions like USB 3.0 require the Extension Pack, free for personal or educational use only, not business use.
Still, it's a near-perfect choice for home users or those looking to experiment with different operating systems for free and easily.
VMware: Maximum power and professional versatility
VMware It is probably the most advanced and mature solution, both in its Workstation/Fusion version (for desktop) and in the ESXi/vSphere business version. Its strength lies in its wide range of Professional features, optimization and customization.
Its main features include:
- Detailed hardware configuration for each VM (RAM, CPU, storage, USB, etc.).
- Cloning, Snapshots, and Linked Clones to save space and speed up deployments.
- Support for 3D graphics advanced: DirectX 11, OpenGL 4.3 and up to 2GB of VRAM.
- Integration with vSphere and other VMware enterprise solutions.
- Additional tools such as VMware Tools, which provide support for clipboard, shared folders, drag and drop, and better overall performance.
VMware Workstation and Fusion are divided into two versions:
- Player: Free for personal use, although with limited features.
- Pro: Paid, with full access to all advanced features, aimed at businesses and professional users.
While it offers excellent performance on all types of systems (Windows, Linux, macOS), the learning curve may be steeper due to the number of advanced options, and the cost of licenses can be a barrier for home users.
Detailed Comparison: Feature Table
To get a quick overview of the differences, here is one comparative table of the most relevant aspects:
| Hyper-V | VirtualBox | VMware (Workstation/Fusion) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hypervisor type | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| License | Included in Windows Pro/Server | Free (GPLv2), paid extensions for business | Free (Player), Paid Pro |
| Host OS | Windows | Windows, Linux, macOS, Solaris, FreeBSD | Windows, Linux, macOS |
| Guest OS | Windows, Linux, FreeBSD | Windows, Linux, macOS, DOS, Solaris, FreeBSD | Windows, Linux, macOS (Fusion) |
| 3D Support | Basic, DirectX 9 | Limited, DirectX 9/OpenGL 3.0 | Advanced, DirectX 11/OpenGL 4.3 |
| USB 3.0 | Yes | Yes (with Extension Pack) | Yes |
| Snapshots | Yes | Yes | Yes (Player no) |
| Shared folders | Yes (more complex) | Yes | Yes |
| Shared clipboard | Yes (MSE enabled) | Yes | Yes |
| Drag and Drop | Yes (MSE) | Yes | Yes |
| Live migration | Yes | Teleporting | Pro: No (vSphere ESXi only) |
| Remote management | Hyper-V Manager, PowerShell, Admin Center | PhpVirtualBox (Web), VBoxManage (CLI) | vCenter (ESXi only), GUI, CLI |
| Extensions/Integration | Windows, WSL, Docker | Extension Pack | vSphere, vCenter, other VMware solutions |
Licensing and cost models
One of the most determining factors when deciding between these platforms is the licensing model and associated costs. Hyper-V It is included in Windows Pro, Enterprise, and Server at no additional cost if you already have a valid license. VirtualBox es free under GPL for personal, professional and educational use, although some paid extensions are required for business environments. VMware Workstation/Fusion offers a free Player version for personal use, but the Pro version, which unlocks all features, is expensive and geared toward professionals and businesses.
The decision may also be based on how much you're willing to invest and whether your environment already has Windows Server licenses or other enterprise tools.
Virtual disk formats and compatibility
A key issue is the compatibility in virtual disk formats and migration between platforms. Hyper-V uses VHD and VHDX formats, but they are not directly compatible with VirtualBox, which supports VDI, VMDK, VHD, and HDD. VMware uses VMDK as its primary format, which is widely recognized and compatible with VirtualBox. All platforms allow importing and exporting VMs in OVF format, although minor incompatibilities may arise depending on the virtual hardware being emulated.
Performance and resource management
El performance of a virtual machine It is heavily influenced by the physical hardware and configuration. However, some differences stand out: VMware excels in advanced graphics support and fluidity, ideal for graphics-intensive environments. Hyper-V It benefits from its integration with Windows, managing resources well in Windows workloads and servers. VirtualBox It is sufficient for basic or home uses, although it may have limitations in graphics acceleration and on older hardware.
Regarding memory management, all support techniques such as ballooning to optimize RAM and allow VMs to be suspended and resumed quickly.
Remote management and automation
Remote control is key in environments with many VMs. Hyper-V allows management through Hyper-V Manager, PowerShell and Windows Admin Center, facilitating advanced automation. VirtualBox It has PhpVirtualBox and VBoxManage for administration on servers without a graphical interface. VMware Integrates with vCenter and CLI tools, offering centralized management in enterprise environments.
The choice will depend on whether you prefer graphical interfaces, web or control via command line. commands.
Virtual networks: Modes and possibilities
Virtual networks in these environments are very flexible, with different modes available: VirtualBox offers NAT, bridge, internal, host-only, etc. VMware includes NAT, bridge and advanced networking in the Pro version. Hyper-V It integrates with Windows virtual switches, supporting bridge, private, external, VLAN and interface grouping, making it very powerful for enterprise scenarios.
If you want to perform complex network testing or simulate infrastructure, any of these options may be suitable, with Hyper-V and VMware standing out for their stability and advanced features.
Additional features and extensions
Each platform offers additional tools: Hyper-V It features Windows Sandbox, Docker and WSL2 integration, and enhanced session mode. VirtualBox It has extensions for USB 2.0/3.0, encryption, VRDP and link cloning to save space. VMware provides advanced cloning, high-resolution support, cloud integration, and centralized management in ESXi environments.
Whenever you install them, remember to apply Guest Additions or VMware Tools to ensure full compatibility with things like shared folders, clipboards, and file drag and drop.
Compatibility and coexistence between hypervisors
It is possible to enable multiple hypervisors on a single system, although with caution. Starting with Windows 10 May 2020 and later, you can activate shared virtualization, but requires compatible hardware and updated versions. However, having Hyper-V enabled can impact VMware or VirtualBox performance, and running multiple platforms simultaneously is not recommended to avoid resource conflicts. It's best to enable only the primary hypervisor you plan to use unless you require specific features from other platforms.
Security, encryption and backups
Security in virtual machines is essential, especially in business environments. All systems allow encrypt virtual disks (in VirtualBox with Extension Pack, VMware with its built-in features, and Hyper-V with BitLocker). External solutions such as BackupChain or NAKIVO Backup & Replication facilitates automatic backups across all hypervisors, ensuring protection and recovery from failures. Additionally, snapshots or checkpoints allow for quick reversion to previous states in the event of a problem.
Which one to choose according to your profile and needs?
There's no one-size-fits-all option, as the best choice will depend on your context. For businesses running Windows, Hyper-V is often the most logical option due to its integration and cost. For developers and multiplatform users, VirtualBox stands out for its flexibility and free availability, with easy setup. For those who require maximum power, advanced graphics, or integration with VMware products, paid solutions such as VMware Workstation Pro or Fusion Pro offer excellent features, albeit at a higher cost.
For home users or those looking to experiment, VirtualBox and the free version of VMware (Player) are usually sufficient. If you're looking for advanced management or enterprise deployments, Hyper-V and VMware's paid options are the best options.
The final decision should be based on which operating systems you need to virtualize, your budget, hardware compatibility, your expertise, and the scale of your deployment. Each platform has strengths that will make one stand out depending on your priorities, and with the information presented here, you can more effectively assess which one best suits you and get the most out of your hardware with virtualization.
Passionate writer about the world of bytes and technology in general. I love sharing my knowledge through writing, and that's what I'll do on this blog, show you all the most interesting things about gadgets, software, hardware, tech trends, and more. My goal is to help you navigate the digital world in a simple and entertaining way.