- macOS recovery mode allows you to repair disks, reinstall the system, and restore Time Machine backups on both Intel Macs and Apple Silicon.
- The boot combinations and Internet Recovery determine which version of macOS is offered and how the recovery utilities are loaded.
- Reinstalling macOS can be done without deleting data, but a full erase using Disk Utility removes accounts, files, and settings.
- Before using destructive options, it is advisable to have backups and, if necessary, use specific data recovery tools.
When macOS starts to cause trouble or your Mac simply doesn't start up as it should, recovery mode and the different macOS recovery options They become your lifeline. From this special environment, you can reinstall the system, repair disks, restore backups, or even connect to the internet to download macOS again without needing a USB drive.
Master all these recovery options It's key to avoiding problems with your data and knowing what to do in every situation: a minor startup failure is not the same as a nearly failed hard drive or the need to erase everything to sell your Mac. In this guide, you'll see, step by step and in detail, how recovery mode works on Macs with Intel chips and Apple Silicon, what keyboard shortcuts exist, what each utility does, how to use Internet Recovery, and what precautions you should take before touching anything.
What is macOS recovery mode and what is it used for?
macOS Recovery Mode It is a minimal system that lives in a hidden partition or is loaded from the internet and includes the MacOS UtilitiesApple introduced it with OS X Lion and it's designed to allow you to recover, repair, or reinstall the system even if the main installation is damaged.
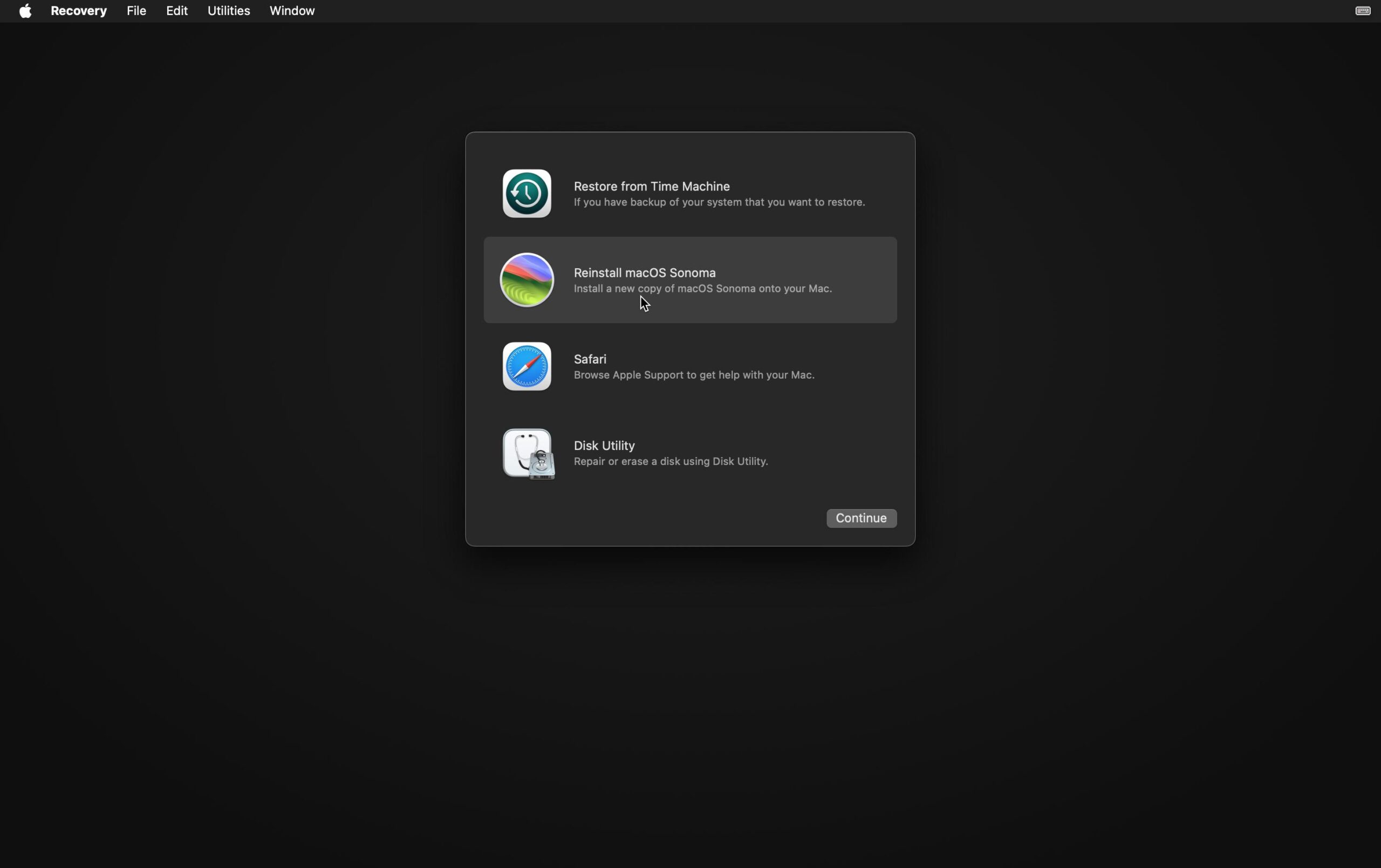
When you start in recovery mode You don't enter your usual desktop, but a small interface where options such as Restore from Time Machine, Reinstall macOS, Disk Utility, and Safarias well as more advanced tools like Terminal. From there you can fix disk errors, format volumes, reinstall the system, restore a backup, or find online help.
This recovery environment It is also the basis for more advanced functions such as Online RecoveryThis downloads utilities and the macOS installer directly from Apple's servers in case the local recovery partition is missing or corrupted. This includes scenarios such as newly replaced or completely erased disks.
In practice, the recovery mode It's the safety net of any Mac: you'll use it to repair boot problemsreinstall macOS (keeping or not keeping your data), prepare a computer for sale, recover files from Time Machine, or diagnose hardware failures when the system no longer responds normally.
Differences between Mac with Intel chip and Mac with Apple Silicon
How to enter recovery mode It depends on the type of processor in your Mac. Today, there are two main families: Macs with Intel processor and the most modern ones with a chip Apple silicon (M1, M2, M3, M4, M5 series…). The utility environment is very similar in both, but the boot process and some security options differ.
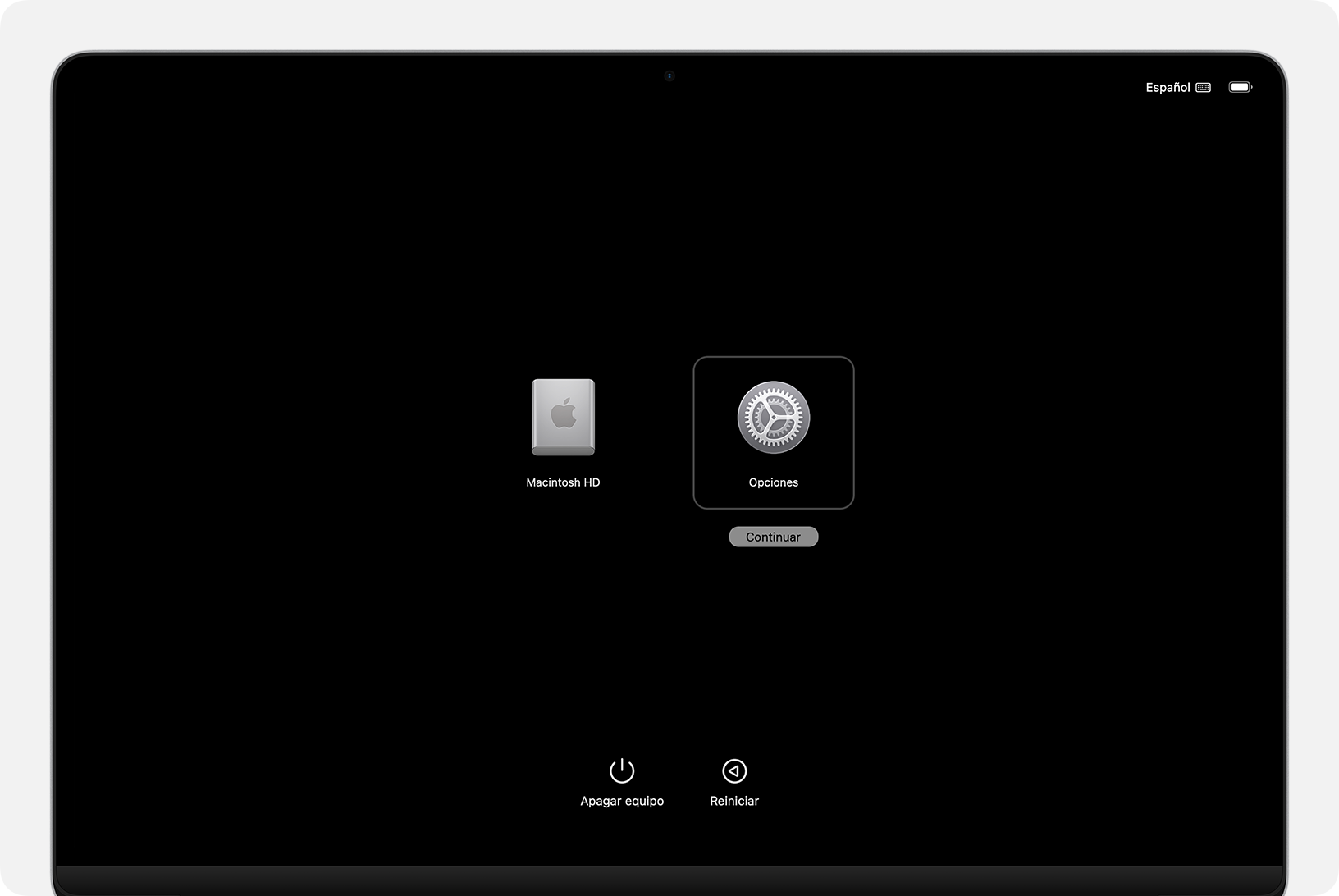
On Macs with Apple SiliconThe power button (or Touch ID on laptops) is the key element. Holding it down while starting up brings up the startup screen. Startup optionsFrom there you can select a boot volume or access Options > Continue To open the recovery utilities. The system automatically detects if Internet Recovery is needed.
On Macs with IntelAccess is granted via key combinations during startup. This is where shortcuts like Command (⌘) + R, Option + Command + R o Shift + Option + Command + RDepending on the combination, the Mac will either load the local recovery partition or boot into recovery from the internet and offer one version of macOS or another to reinstall.
If you're not sure what chip your Mac has,Apple recommends trying both methods: either hold down the power button until you see "Loading startup options" (typical of Apple Silicon) or turn on and hold Command + R (typical of Intel). None of these attempts will damage the computer; you'll simply see one screen or the other.
Beyond the startup, both types of Mac They share the same main utilities: Time Machine, Reinstall macOS, Disk Utility, and SafariIn addition to advanced tools, the difference lies in certain boot security settings that are managed from recovery mode in Apple Silicon.
How to enter recovery mode on a Mac with Apple Silicon
On a Mac with an Apple Silicon chip (M1, M1 Pro, M1 Max, M2, M3, etc.), accessing recovery mode is fairly straightforward, but it's advisable to follow the steps exactly for the options to appear. Startup options and macOS does not start normally.
First, make sure your Mac is completely turned off.If your device freezes and becomes unresponsive, press and hold the power button or Touch ID for up to 10 seconds until the screen turns off completely. On laptops, Touch ID also acts as the power button, so simply press and hold it.
Next, press and hold the power button again.Don't let go as soon as you see the logo: keep pressing it until the message appears. "Loading startup options" or you see the screen with the boot disk icons and the icon of OptionsOnly then do you release the button.
On the boot options screen, Click on Options and then on the button ContinueThe system may ask you to select the volume you want to recover (for example, "Macintosh HD") and to choose a user account whose password you know in order to continue with administrative privileges.
After entering the user passwordThe Mac will finish loading the Recovery environment and you'll see the classic macOS Utilities window with the different options: restore from Time Machine, reinstall macOS, access Safari, open Disk Utility, or use other tools like Terminal.
When you finish using recoveryYou can exit simply by opening the Apple menu at the top and choosing Restart o DeleteIf your Mac later starts up with a blank screen, an exclamation mark in a circle, or another strange symbol, you should check Apple's documentation on Macs that fail to start up, as there could be a more serious hardware or disk problem.
How to access recovery mode on a Mac with an Intel processor
On Macs with an Intel processorAccess to recovery mode is done using keyboard shortcuts while the computer is booting. It's important that the keyboard is recognized in time, especially if it's wireless or a third-party keyboard.
As a first step, shut down your Mac completely.If it's locked, press and hold the power button until it turns off. Once it's off, press the button again to turn it on, and as soon as you hear the startup sound or see the screen begin to light up, press and hold the Command (⌘) + R keys without letting go.
You must hold Command + R down until the Apple logo, a rotating globe icon, or the macOS Utilities window appears on the screen. If the system does not locate the internal recovery partition, you can proceed directly to trying the Online Recovery, which is indicated by that rotating globe.
If your Mac asks you to select a Wi-Fi networkChoose one from the network menu list or connect an Ethernet cable. For secure networks, you'll need to enter your password. A good internet connection is crucial, as your computer may need to download recovery components or even the full macOS installer.
Once inside the recovery environmentThe process is similar to Apple Silicon: you may be asked to choose a volume to recover (for example, "Macintosh HD") and a user account whose password you know. After these steps, a window will open with macOS utilitiesFrom there you can repair disks, reinstall the system, restore backups, or browse with Safari to find help.
You can close the recovery at any time. using the Apple menu > Restart o DeleteIf your Mac doesn't start normally afterward, it's a good idea to repeat the procedure and use Disk Utility to check the disk's health before performing a full reinstallation.
Advanced boot combinations and macOS versions
In addition to the classic Command + ROn Intel Macs, Apple offers several keyboard shortcuts that change which version of macOS is suggested when reinstalling from recovery mode. This is useful if you want to revert to the original system version, keep the current one, or install the latest compatible version.
Command (⌘) + R It's the standard combination: it loads the local recovery partition (if one exists) and allows you to reinstall the version of macOS you already have Installed on your Mac, it's ideal for repairing system files without changing the version. It doesn't delete your data by default; it only rewrites the system.
Option (⌥) + Command (⌘) + R force the Online Recovery To install the latest version of macOS compatible with your Mac model. This is the recommended option if you want to update to the most recent version possible without going through the Mac App Store or creating USB installers.
Shift + Option (⌥) + Command (⌘) + R try downloading from the internet the version of macOS that came pre-installed with your Mac or the nearest one still available. It's very useful for restoring the computer to its factory settings, for example, before selling it or giving it to someone else.
In Apple Silicon, the system manages internally These variations depend on the state of the disk and the configuration, but the idea is the same: the Mac can offer to reinstall your current version, the original version, or the latest compatible version, downloading it from Apple's servers if necessary.
Internet recovery on macOS: how it works and requirements
Online Recovery It's a special mode where the Mac downloads the recovery utilities and macOS installer directly from Apple's servers, instead of relying solely on the local recovery partition on the internal hard drive. This is crucial when the hard drive has been replaced, completely formatted, or the recovery partition is damaged.
Not all older Macs have this option enabled by default.Models manufactured from late 2011 onward that run OS X 10.7 Lion or later typically include it without any modifications. For slightly older devices, Apple released EFI firmware updates that added Internet Recovery support to models such as Late 2010 MacBook Air, mid-2010 MacBook and MacBook Pro, 2010 Mac mini, or 2010 iMac.
At the network level, internet recovery is quite finicky.Your router must be configured with DHCP (automatic IP assignment) and use WPA / WPA2 as a Wi-Fi security protocol. It does not work correctly on networks that use WEP, WPA-Enterprise, PPPoE connections managed directly by the Mac, or networks that require accepting terms and conditions on a captive portal typical of cafes, gyms, or shopping malls.
When the local recovery partition failsThe Mac usually displays a rotating world globe with a message indicating that recovery is initiating from the internet, accompanied by a progress bar. You can also force this mode with the following combinations. Option + Command + R o Shift + Option + Command + R on Intel Macs.
If the balloon appears accompanied by an exclamation mark or warning symbolThe problem is usually with the network connection: the download has been interrupted, the network is incompatible, or there's a temporary outage. In that case, try a different Wi-Fi network, use Ethernet if possible, check your router settings, or try again later.
What you can do inside macOS recovery mode
Once inside macOS UtilitiesRecovery mode offers a set of tools designed to troubleshoot problems without the need for third-party applications. Although the environment is limited, it's sufficient for repairing the system, managing disks, and restoring data.
Reinstall macOS Download and reinstall the operating system on your chosen disk. In standard mode, only system files are rewritten, preserving your user accounts, apps, and documents. This is a way to "clean" macOS when it has become corrupted or has accumulated errors without formatting everything.
Safari within the recovery It gives you limited internet access to consult Apple support pages or search for technical solutions. It doesn't support extensions, add-ons, or advanced bookmarks, but it's sufficient for reviewing official documentation or guides while you repair your Mac.
Disk Utility It is the key tool for repair, erase or partition disks. Includes the function First Aid to verify and repair file systems, as well as options to erase volumes (e.g., in APFS format) or manage containers and partitions before a clean reinstall.
In addition to these four main optionsThe menu bar usually provides access to advanced tools such as Bus Terminal (for command-line operations), boot disk selector, system security options, network settings, and other utilities geared towards administrators and advanced users.
Reinstall macOS without losing data vs. erase and reinstall from scratch
Reinstalling macOS is not the same as erasing the diskIn most cases, if you choose the option to Reinstall macOS From recovery mode, and pointing to the system volume (usually "Macintosh HD"), the installer simply... replace operating system files for a fresh copy, keeping your files and accounts.
This type of complete reinstallation It's more thorough than a simple update. Instead of just changing the new parts of the latest version, the installer rewrites the entire system, helping to fix accumulated damage, beta bugs, or rare glitches that aren't addressed by a normal update.
If what you want is leave the Mac like newYou'll have to go one step further: start in recovery mode, open Disk Utility, select the system volume or group of volumes, choose Format APFS format and use the option "Delete volume group"This deletes user accounts, network settings, and all files and folders.
Once the deletion is complete, close Disk Utility and return to the main window to select Reinstall macOS by clicking on Continue and follow the instructions until the installation is complete. When finished, the Mac will behave as if it were brand new, prompting you for initial setup.
In either scenario (reinstalling without deleting or formatting and reinstalling) is essential to have a updated backupAlthough reinstallation shouldn't affect your data, there's always a risk of errors, power outages, disk failures, or network problems that could lead to data loss.
Recommendations for the keyboard and recovery boot
For the boot key combinations to work properlyThe Mac should recognize the keyboard very early during startup. Sometimes, if the keyboard isn't detected in time, the keys have no effect and the computer starts normally, which can give the impression that recovery mode "isn't working."
On Mac laptops, the most reliable is to always use the integrated keyboard For these operations. On desktop computers like iMac or Mac mini, if you're using an external keyboard, it's best to wait one or two seconds after pressing the power button before entering the key combination, so the system has time to detect it.
With wireless keyboards (Bluetooth) It's normal for the connection to take a little while to establish. If you're having problems, try connect the keyboard via cable While booting into recovery mode, use a simple, Mac-compatible USB keyboard to minimize errors.
If your keyboard is a PC keyboardWith the Windows key instead of the Command key, the key mapping can be confusing. In that case, a keyboard designed for Mac will save you trial and error time, especially when you need to use more complex shortcuts like Shift + Option + Command + R.
If after checking keyboard, combinations and network If recovery mode still won't load, the recovery partition may be damaged or the disk may have physical problems. In these cases, Internet Recovery or even a USB installer created from another Mac They can be the alternative.
Use Disk Utility in recovery mode to repair and erase
Before you rush to format or reinstallIt's worth trying Disk Utility from recovery mode to check for errors in the disk or file system that can be repaired without deleting anything.
From the macOS Utilities window, Select Disk Utility and click on ContinueIn the sidebar, you'll see the physical disks and logical volumes (APFS, containers, etc.). Select your system's primary volume (usually named "Macintosh HD" or something similar) and click on First Aid to analyze and repair logical errors.
If First Aid doesn't solve the problem If the drive has serious errors, you may need to perform a full erase. To do this, select the system volume or volume group, and click on Delete and choose as format APFS (for recent systems). If the option appears, use "Delete volume group" to remove the entire macOS-related set.
When the deletion process is completeDisk Utility will display the new, clean volume. Press AcceptClose the app from the menu Disk Utility > Quit Disk Utility and return to the main window to select the reinstallation of macOS on that newly created volume.
Always keep in mind that deleting with Disk Utility It deletes accounts, network settings, documents, photos, and any other data stored on that drive. If you didn't have a backup beforehand, it's still possible to try to recover information using specialized software by booting from another drive, but the risk of data loss is high.
Recover data before touching the system: backups and recovery
Whenever possible, the prudent thing to do It's important to save your data before performing any aggressive operations in recovery mode. A simple reinstallation while keeping your data is usually safe, but if you're going to erase the disk or suspect the drive is failing, a backup can make all the difference.
If you can still log in to macOS, make a backup with time Machine to an external drive or manually copy important files to another drive, in addition to noting your network settings (SSID, Wi-Fi passwords, special settings) so that you can rebuild them later without any headaches.
When your Mac won't start upOne option is to use data recovery applications for Mac that allow you to create a external boot diskThe typical workflow involves installing the software on another Mac, preparing a bootable USB drive with the recovery environment for that tool, starting the broken Mac from the USB drive, and scanning the internal disk to extract files to another external drive.
This type of recovery solution This is especially useful if you've experienced an accidental format, a failed macOS update, a malware attack, or a system crash that has rendered the drive inaccessible. Even so, the more the drive is used after the loss, the harder it will be to recover everything, so it's best to act as soon as possible.
Even in the most complicated scenarios (severely damaged disks, Macs that won't boot even with recovery), a professional recovery service or Apple's authorized support can offer alternatives, albeit at a higher cost. That's why insisting on regular backups with Time Machine remains the best insurance policy.
Learn about all macOS recovery options —from local recovery mode to Internet Recovery, including advanced boot combinations, Disk Utility, and the ability to reinstall with or without prior erasure— allows you to react calmly when your Mac fails and choose at any given moment the least aggressive strategy for your data and the most effective way to restore system stability.
Passionate writer about the world of bytes and technology in general. I love sharing my knowledge through writing, and that's what I'll do on this blog, show you all the most interesting things about gadgets, software, hardware, tech trends, and more. My goal is to help you navigate the digital world in a simple and entertaining way.