would you like to know how putting textures in AutoCAD 2D? Most designers, architects and students know very well what this digital design tool is for. But, have you ever wondered how to put textures in AutoCAD in the 2D version? Don't worry anymore, here we will leave you the simplest methods so that you become an expert in the subject.
4 methods to put textures in AutoCAD 2D
As you can see, the AutoCAD 2D version is a bit more complicated when it comes to placing textures. That's why we've brought you the 4 options for placing textures in AutoCAD 2D:
Here you can learn about: How to Convert AutoCad to Older Versions Online
Method 1: Add a pattern to a surface
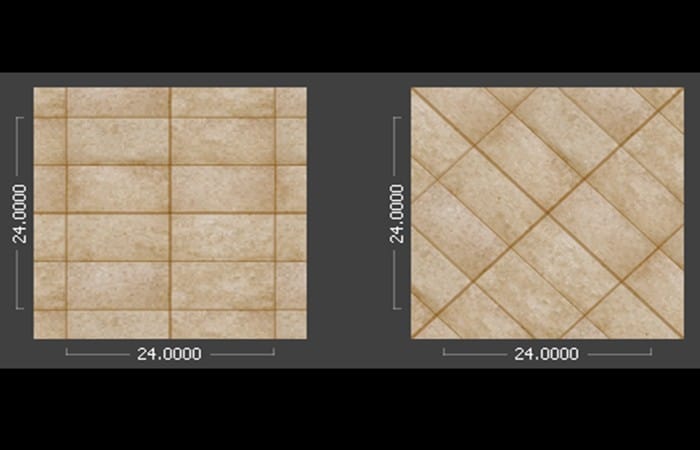
- Step 1:: Open the file in which you are going to putting textures in AutoCAD 2D. Head over to add a pattern in the living room to represent an inlay floor made up of 8″ by 8″ tiles.
- Step 2:: Activate the reference button to their in the status bar.
- Step 3:: Select the layer Am-Hatching so that it becomes Present.
- Step 4:: Activate the command Lined and then in Hatching in the deploy option.
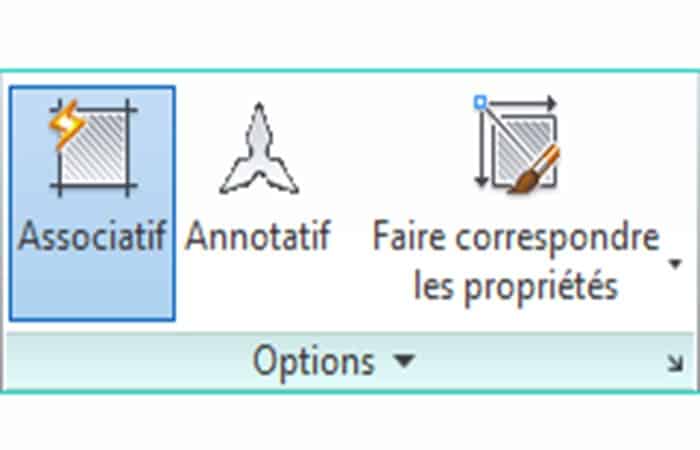
- Step 5:: Enable associative in the panel Ribbon Options.
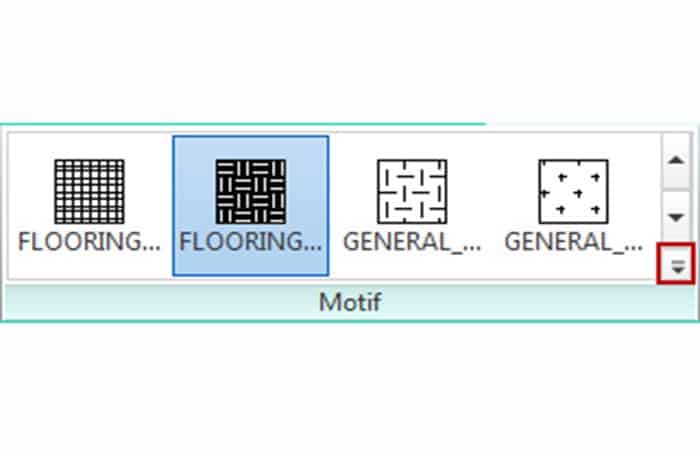
- Step 6:: Select the type of plot Flooring_Parquet in the Ribbon panel pattern.
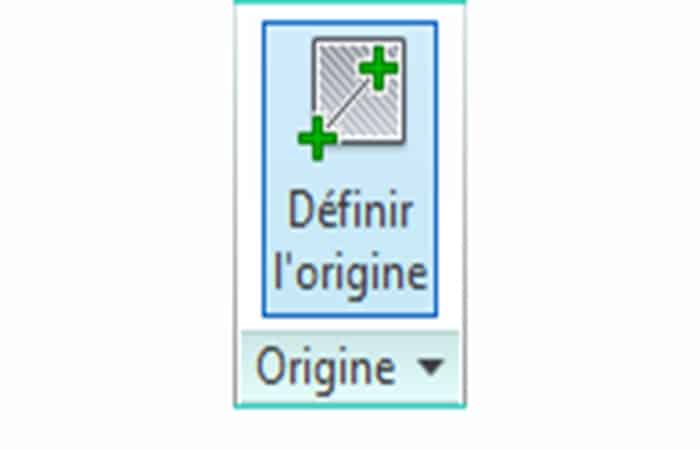
- Step 7:: Click Set origin to determine the origin point of the shading.
- Step 8:: Click Finalize in the upper left corner of the living room.
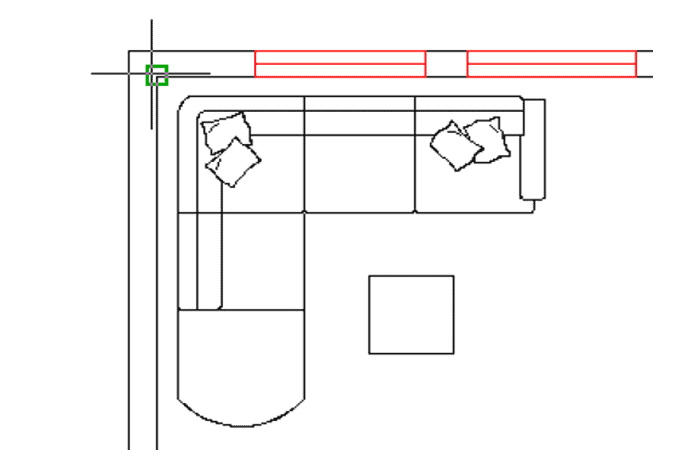
- Step 9:: Click on the living room floor, then click Close shading creation.
Enter the command:
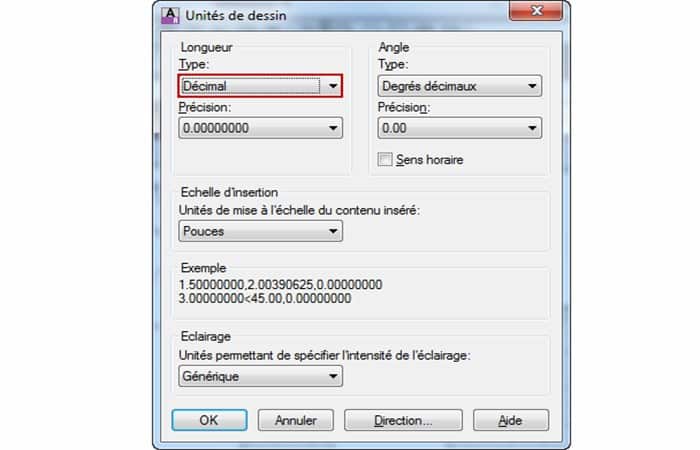
- Step 1:: Activate the command Units. You will need to adjust the size of the tiles precisely.
- Step 2:: select the type of measurement Decimal and do click en Accept.
- Step 3:: Activate the command Distance.
- Step 4:: Click Final point in the top right corner of a tile.
- Step 5:: Then click Final point in the lower left corner of the same tile.
- Step 6:: You should see that the size of each tile is 12″ (1′-0″). However, here we changed the format tile to 8″. You will need to change the shading scale. To modify the floor shadings, double-click on them. The ribbon Shadow Editor which appears at the top of the screen.
- Step 7:: Determines the shading scale with Quick Calculator.
Using the Quick Calculator
- Step 1:: Select the number entered in the box Scale and enter .667.
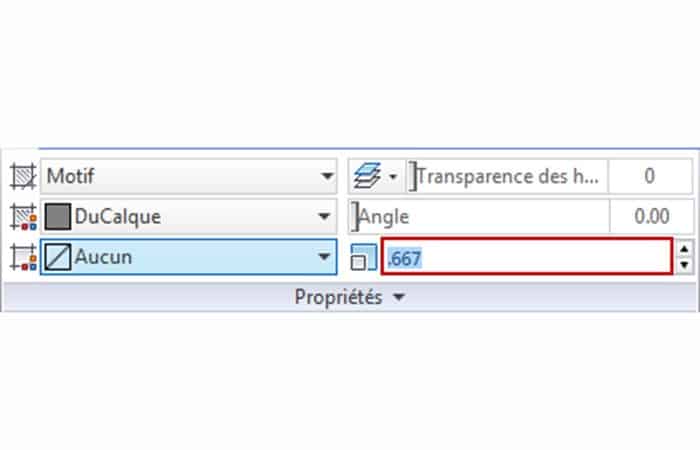
- Step 2:: Click Close Create Shading.
Method 2: Working with texture controls
Each texture type has a unique set of controls, or channels, that adjust properties such as reflectivity, transparency, and self-illumination. In each of these channels, you can assign, hide, or remove textures.
When you assign textures to a material color, the texture colors replace the diffuse color of the material. When you apply a texture, you can realign it to a face or shape by adjusting the material map overlay.
NOTE: : When enabled Textures uncompressed, the amount of memory required to open the drawing increases and textures are created with the best quality. Disabling the Textures option Uncompressed will reduce the quality of images on screen and require them to be compressed before displaying, which increases loading times. Image quality remains unchanged during rendering.
There are two types of textures available: image textures and procedural textures.
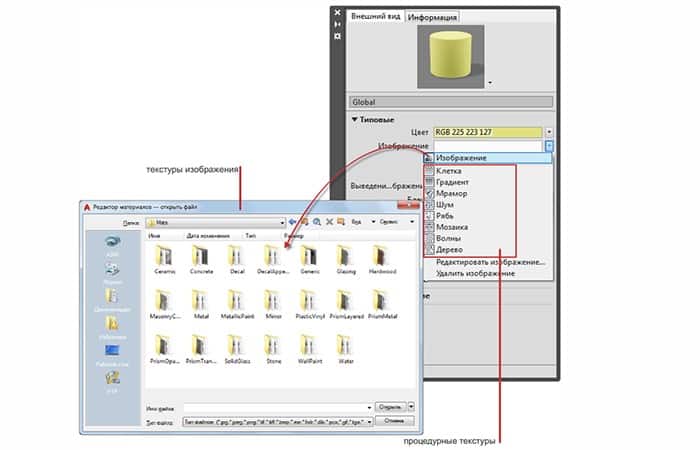
Image textures
Use an image to represent the texture. For example, you can use an image of wood, cinder blocks, metal, carpet, or wicker.
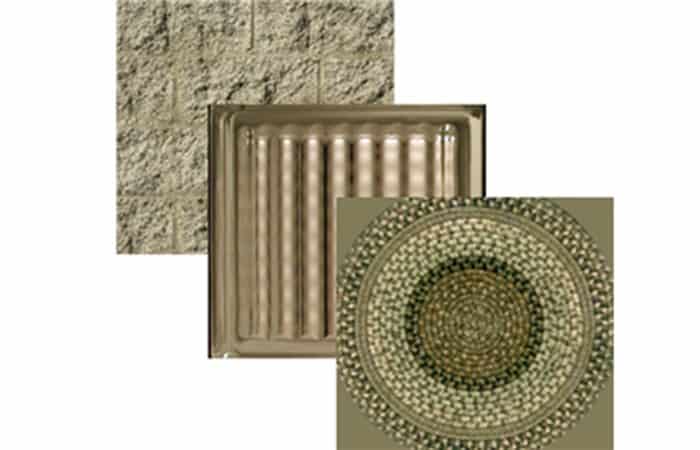

You can edit the texture scale and other properties to customize textures specifically for your model. The product provides a library of images that can be used for textures. You can also add your own textures using the following file types:
- BMP, RLE or DIB
- GIF
- JFIF, JPG or JPEG
- P
- PNG Image
- TGA
- Fight
Procedural textures
Procedural textures, created using a mathematical algorithm, are used to represent repeating textures such as tile or wood. You can adjust the texture properties to achieve the desired effect.
- E.g.: You can adjust tile size and grout thickness in masonry, or change fiber spacing in wood texture.
The types of settings for procedural textures can vary. They are used to create more complex and realistic textures for the material. These are the ones you can find:
- Marble: You can apply a veined stone pattern to the material. You can also specify the color of the stone and the veins, or change the distance between the veins and their thickness.

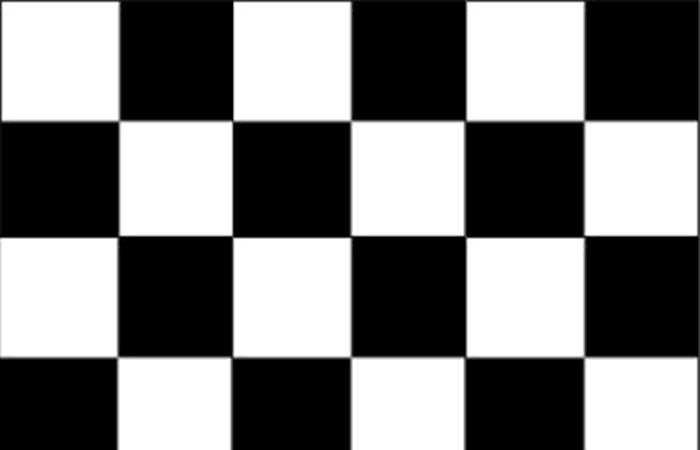
- Checkers: You can apply textures in AutoCAD 2D using a two-color checkerboard pattern to the material. By default, the checkered texture uses a pattern consisting of black and white squares. For components, you can set any color and texture.

- Stains: Here you can put textures in AutoCAD 2D to create a mottled surface pattern. The interleaved texture is recommended for creating granite or similar surfaces.
- Waves: Imitation of the surface of the reservoir. The texture «Waves» is created by forming multiple epicenters of spherical waves and randomly propagating them in a sphere. You can change the number of wave sets, amplitude, and speed of wave propagation. This texture is effectively used as a diffusion and roughness property or in combination with an opacity property.
- Roof tile: Colors are placed in the form of placed bricks or tiles or other materials. It is a good way to put textures in AutoCAD 2D.
- Noise: Here you can create arbitrary distorted surfaces by combining two colors and textures. You can also use the texture Noise to reduce repetition of individual elements.

- Wood:Wood Card is a good choice for texturing in AutoCAD 2D. This style is used to create the color and grain pattern of a wood surface.
- Degraded: With this texture you can create custom gradients that use multiple colors to create graduated tones or color transitions.
Method 3: Change texture properties
The third method for putting textures in AutoCAD 2D is by changing the texture properties to adjust the scale and create complex patterns. To change the texture properties, you can use the Texture editorTo open it, in the Material Editor, you have to double-click on the texture sample.
Texture preview: Any changes made to the parameters are displayed in the sample preview area. You can drag the corner of the preview image to zoom in or out.
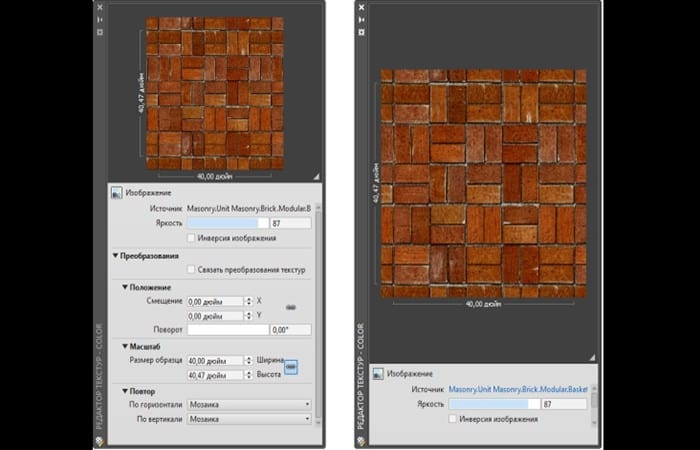
Format: Appearance options are active only for procedural textures.
Transformation: position, scale and repetition
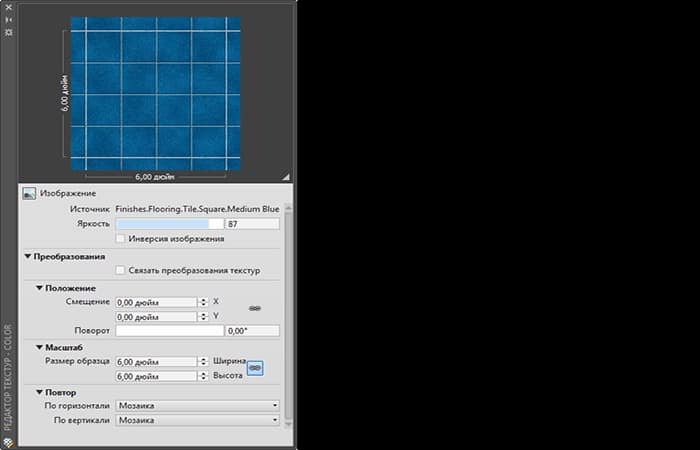
Position, Scale, and Repeat are the three standard transformations used on textures. The following list shows which textures have these attributes associated with them.
- Texture Type: image
- Position: si
- Scale: si
- Reiteration: si
- Texture Type: Mosaic
- Position: si
- Scale: si
- Reiteration: si
- Texture Type: Degraded
- Position: si
- Scale: si
- Reiteration: si
- Texture Type: Cells
- Position: si
- Scale: si
- Reiteration: si
- Texture Type: Interference
- Position: si
- Scale: No.
- Reiteration: No.
- Texture Type: Waves
- Position: si
- Scale: No.
- Reiteration: No.
- Texture Type: Wood
- Position: si
- Scale: No.
- Reiteration: No.
- Texture Type: Stains
- Position: si
- Scale: No.
- Reiteration: No.
- Texture Type: Marble
- Position: si
- Scale: No.
- Reiteration: No.
Position ownership changes
To apply position, scale, and repeat property changes to the current texture, select Link texture transformations for other textures of the same material.
- Position. Each texture has a material shift and rotation factor. You can control the material coordinates in the sample and rotate the image around the W axis in the coordinate system UVW.
NOTE: : UVW corresponds to the three axes of texture space, like the XYZ axes in other coordinate systems. Textures use UV coordinates to project an image onto a surface. Coordinate values greater than 1 result in a repetition of the texture ("tiling"), overlaying virtually the same coordinate space from 0.0.0 to 1.1.1. UV coordinates are not limited to values between 0 and 1. They can contain arbitrary values, positive or negative.
Rotated texture
- Scale. Sets the actual units to use for scaling.

Scaled texture
- Reiteration. The command is used Mosaic to apply and repeat an image in a pattern. This effect is used to create a tiled floor or fountain.

Repeatable texture
Mosaic fills the selected object with texture images. Since the texture is scaled to the size of the object, it may be necessary to change the UV coordinate system or rotate the texture to see the mosaic effect.
Method 4: Putting textures in AutoCAD 2D and adjusting the material combination on objects and faces
After applying the texture to the material, you can adjust the orientation of the texture to fit the shape.
Adjust texture to fit shape
Textures can be adjusted to fit the shape of objects. You can use the material overlay feature for this. The blending adjustment reduces the pattern distortion effect.
- Flat overlay. Overlays the image as if it were projected onto a 2D surface. The image is not distorted in the projection direction, but is distorted when projected onto a curved surface and when viewed from an angle. If the image is not scaled, this overlay is typically used for flat faces.
- Cubic covering. Image overlay on the body of the box. The image is repeated on all sides of the object.
- Spherical coating. Image overlay on a spherical object. The top and bottom edges of the map are compressed to a point at the sphere's "north and south poles."
- Cylindrical coating. Image overlay on a cylindrical object. Not the top and bottom edges are folded and connected, but the horizontal edges. The image height is scaled along the axis of the cylinder.
Using a Blending Gizmo to Adjust the Texture
To make further adjustments to the material blend, you can use the Blend Gizmo to move or rotate the texture map on the object. To display it, select the textured object and enter MATERIALSOTV.
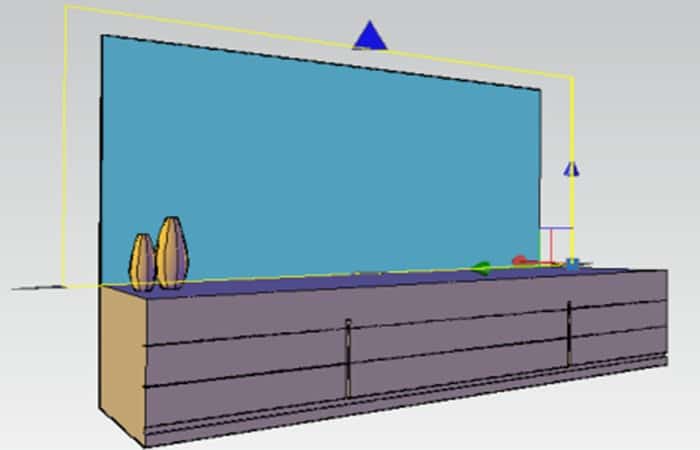
Adjust, move, and rotate the texture by dragging the gizmo's axes.
You may also like: How to Measure Arc Length in AutoCAD
As you can see, adding textures in AutoCAD 2D is very simple if you follow the methods and steps we show you. There are thousands of ways to add textures in this version of AutoCAD, but considering the complexity, we recommend you start with these. We hope we have helped you.
My name is Javier Chirinos and I am passionate about technology. Ever since I can remember, I have been interested in computers and video games, and that passion has turned into a job.
I have been publishing about technology and gadgets on the Internet for over 15 years, especially in mundobytes.com
I am also an expert in online marketing and communication and have knowledge in WordPress development.