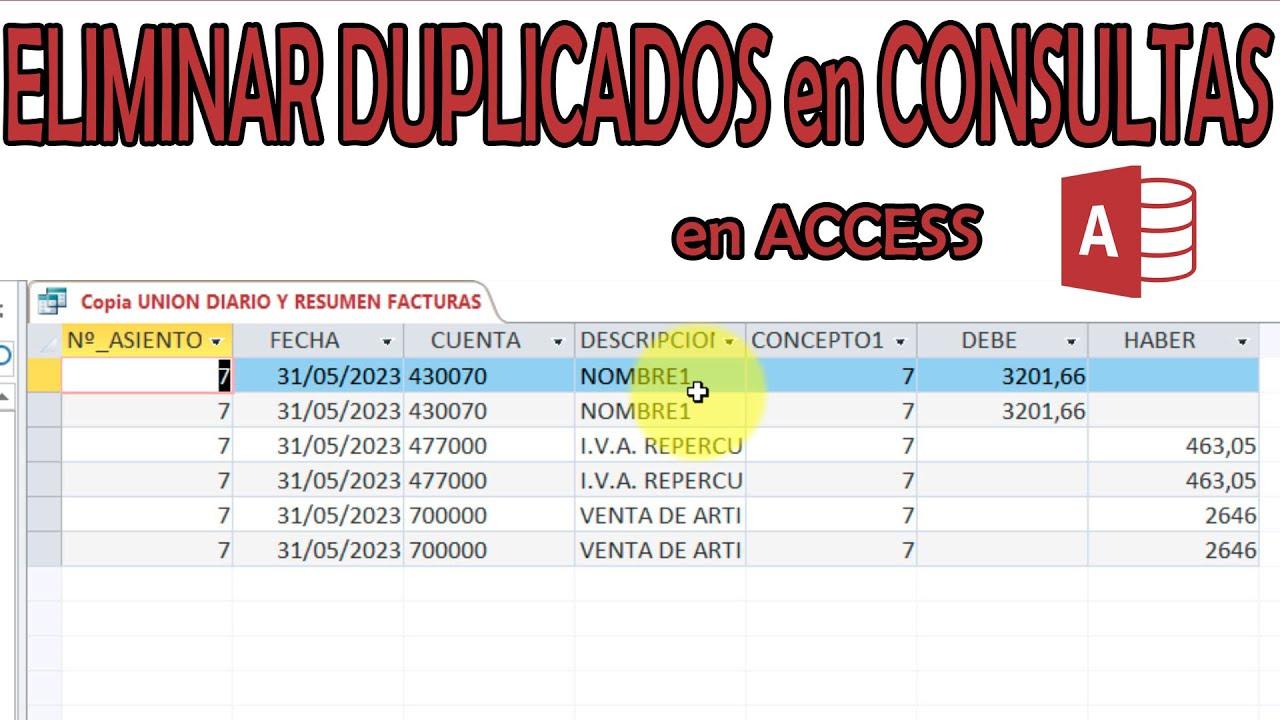
- Duplicate data distorts analysis and decisions, so it is essential to detect and control it before working with it.
- Spreadsheets like Excel allow you to highlight, filter, and remove duplicates by combining conditional formatting, advanced filters, and text functions.
- En databases SQL, SELECT DISTINCT and alternatives like GROUP BY help obtain results without repeated rows without modifying the original data.
- Bibliographic management tools and good backup and pre-review practices reduce the risk of losing relevant information by eliminating duplicates.
When you work with databases, spreadsheets or information systems, the Duplicate data can become a real headacheRepeated records, names spelled in a thousand different ways, poorly formatted dates, or extra spaces make the analyses unreliable and waste your time manually checking what the system could help you clean up in seconds.
The good news is that there are Powerful tools for locating, highlighting, and removing duplicate data both in Excel and Google Sheets as in SQL databases or bibliographic management tools. Understanding how they work, how they differ, and what risks they pose (such as deleting information you might later miss) is key to keeping your data organized and being able to analyze it with peace of mind.
Why do duplicate data appear and why are they a problem?
In practice, Duplicates arise from human error, repeated imports, or poorly coordinated systems.Forms that are submitted twice, files that are combined without prior cleaning, or integrations between applications that do not properly validate the information are the perfect breeding ground for your system to become filled with duplicate records.
Besides the obvious duplicates, you will find slight variations that actually represent the same dataNames with mixed uppercase and lowercase letters, extra spaces, different abbreviations, or dates with different formats that the system does not recognize as the same, even though it is obvious to a person that they refer to the same thing.
The impact is significant: The statistics are distorted; customer or patient counts are inflated.Emails are repeated in email campaigns, invoices are duplicated, or the number of orders is overestimated. This can lead to poor decisions, extra costs, and a significant lack of trust in data quality.
Therefore, before diving into creating dashboards or advanced analyses, it's worth investing time in a Excellent data cleaning tool for detecting and correcting inconsistenciesRemoving duplicates is a central part of this process, but not the only one: you also have to homogenize text, remove strange spaces and normalize dates.
Detect and highlight duplicate data in spreadsheets
Tools like Excel offer very convenient functions for to quickly identify which values are repeated in a range of cellsBefore deleting anything, it's advisable to use a visual format that helps you review and calmly decide what you want to keep.
A very common way to start is by... Conditional formatting to highlight values that appear more than onceThis way, you don't change the content of the cells, you simply mark them so you can analyze them.
The typical workflow involves first selecting the cells to be reviewed and then applying a Conditional formatting rule that marks duplicates with a different background color or fontThis allows you to identify patterns: for example, to see if a person appears multiple times in a customer list or if certain product codes have been registered more than once.
Furthermore, you can combine this automatic highlighting with filters within the spreadsheet itself to View only rows affected by duplicates and review them one by one.This gives you control and reduces the risk of accidentally deleting important information.
Safely remove duplicate values in Excel
Once you're clear on which repetitions are unnecessary, Excel includes a specific function called “Remove duplicates” which permanently deletes repeated rowsThis is where you have to tread carefully, because what you delete is not easily recovered if you haven't saved a copy.
Before running this tool, it is highly recommended Copy the original data range to another sheet or backup fileThis way, if the cleanup produces an unexpected result, you can review what you've removed and recover information without any problems.
The procedure is based on selecting the range of cells you want to clean and then indicating which columns the values should be compared in to decide if a row is duplicated. If you select multiple columns, only the row whose complete combination matches another row will be considered a duplicate.which is very useful when working with complex data.
Upon confirming the operation, Excel removes the extra rows and It shows you a summary of how many duplicates have been deleted and how many unique records remain.This short report helps you validate whether the results match what you expected when you started the cleaning.
It should be borne in mind that Filtering unique values is not the same as removing duplicates.When you filter, duplicate rows are only temporarily hidden, but they're still there; removing duplicates deletes them completely. That's why starting with a unique filter or conditional formatting is a more prudent strategy.
Criteria for considering a value to be duplicated
When spreadsheet tools compare duplicates, They do so based on what is actually seen in the cell, not on the underlying interpreted value.This has some curious consequences that you need to know so you don't get any surprises.
For example, two dates that represent the same day may not be considered duplicates if One is written as “08/03/2006” and the other as “March 8, 2006”because the text content is different even if the meaning is identical. The same can happen with names and strings with different spaces or capitalization.
Similarly, a number stored as text and the same number in numeric format They can be treated as different values. That's why it's so important to normalize formats before attempting to delete duplicate rows en masse.
Before performing an aggressive cleanup, it's worth first filtering for unique values or using conditional formatting to confirm. that the comparison criterion is working as you thinkSetting these rules of the game at the beginning prevents losing valid data or leaving disguised duplicates.
Text functions in spreadsheets to clean dirty data
A huge part of the problems with duplicates doesn't stem from the exact same value being repeated, but from the fact that The same information is written in slightly different waysThat's where Excel or Google Sheets text functions come into play to standardize and prepare the ground before removing repetitions.
It's very common to find columns where some names are in uppercase, others in lowercase, and others mixed randomly. To unify them, you have functions that They convert everything to lowercase, everything to uppercase, or only capitalize the first letter of each word.This ensures that “ANA PÉREZ”, “ana pérez” and “Ana Pérez” are treated the same way.
Texts with extra spaces, both within the chain and at the beginning or endA specialized function can remove extra spaces and leave only a normal space between words, thus eliminating "Juan García" or similar phrases that break comparisons.
For data that's closely packed together, such as combined codes or names and surnames in the same cell, it's useful to use extraction and union functions. You can extract a portion of the text indicating from what position and how many characters you want to extract or join several strings into one to reconstruct more coherent fields.
In the case of dates, if they arrive as text with different styles, it's a good idea to transform them into a standard date format based on year, month, and dayThis way, spreadsheets treat them as real dates, you can sort them correctly, and comparisons no longer depend on the cell's visual appearance.
Filter unique values and remove duplicates in spreadsheets
In addition to formatting tools and text functions, both Excel and Google Sheets allow Quickly filter to see only unique values from a column or a set of columnsThis is a very effective way to review results before making irreversible decisions.
In some environments, you can use advanced filtering options to indicate that you only want to show rows with unique values in one or more specific columns. This filtering does not delete data, it simply temporarily hides duplicates., which makes it a very prudent intermediate step.
Once you've confirmed that the unique view is the one you're interested in, you have commands specific to Remove duplicates directly from the data menusTypically, you access something like "Data > Remove Duplicates", where you choose which columns to base the comparison on.
Another option is to use conditional formatting to highlight both duplicates and unique values, depending on your needs. For example, you can: Highlight in a bright color the rows that appear only once and analyze whether they are atypical records, loading errors, or simply infrequent cases that need to be preserved.
If you work with dropdown lists or data validation, it makes a lot of sense to clean them up as well. You can do this through validation menus. define closed lists that prevent the introduction of typographic variations, thus reducing the occurrence of false duplicates that are actually just typos.
Cleaning duplicates in SQL databases with SELECT DISTINCT
When we moved from the world of spreadsheets to the world of databasesThe approach changes slightly. In SQL, one of the first tools for managing repeated information is the operator DISTINCT, which is used in conjunction with the SELECT command to return rows without duplicates in the results of a query.
The idea is simple: when constructing a SELECT statement, you can add the DISTINCT keyword to indicate that You only want one occurrence of each combination of values in the selected columns. This way, if the same logical row is repeated several times in the table, the query will return a single line.
It's important to understand that SELECT DISTINCT does not delete anything from the database: It only affects the result you see when you run the query.The original information remains unchanged in the tables, which is perfect for exploratory analysis where you don't want to modify data yet.
As for the syntax, the general pattern consists of combining SELECT DISTINCT with the list of columns you are interested in, followed by the FROM clause to indicate the table and, optionally, a WHERE clause to filter by specific conditionsThis way you can request, for example, unique customers from only one country or different products from a specific category.
This approach is very useful when you want to narrow down results to non-duplicated entries, whether for Obtain a list of customers without duplication due to multiple orders, display a list of distinct product codes or generate a count of unique items in a dataset.
Differences between DISTINCT and other ways to avoid duplicates in SQL
Although DISTINCT and UNIQUE may sound similar, They do not play the same role within the SQL ecosystemDISTINCT acts in SELECT queries, affecting the rows returned; UNIQUE is usually related to restrictions in the definition of tables, indicating that certain fields cannot contain repeated values.
Furthermore, in contexts with large amounts of data, using SELECT DISTINCT can be performance-intensive, because The database engine needs to compare all selected columns. to determine which rows are the same. In large tables or tables with many columns, this can become cumbersome.
Therefore, in some cases it's worth considering alternatives. One of the most common is to use GROUP BY to group rows by one or more columns and apply aggregation functions (such as COUNT, MIN, or MAX) that allow you to summarize the data efficiently.
You can also rely on clauses like EXISTS for check if certain values are present in another tableThis avoids joining unnecessary duplicate rows. Or, you can use subqueries with well-defined SELECT, FROM, and WHERE clauses to better specify which records you want to retrieve.
When you want to count how many unique values there are in a column, it's common to combine COUNT with DISTINCT, so that You get the number of different elements directly. without needing to check each one of them manually.
Practical examples: customer inquiries and addresses without duplicates
Imagine you're working with an order table where each row represents a purchase made. It's common that The same customer will appear multiple times if they have placed more than one order.If you only want to see each customer once, SELECT DISTINCT is a very clear tool.
In this scenario, you would build a query that selects the customer identification columns (for example, their ID and their name) and apply DISTINCT to receive a list with each client only once., although the original table has ten different orders.
Something similar happens if you need to see all the unique shipping addresses to which products have been sentIf each order includes an address, the table will be full of repetitions; however, with DISTINCT in the address columns you can generate a compact list of shipping points.
When you want to focus on customers from a specific area, you can add a WHERE clause to indicate, for example, that You are only interested in records from a specific countryIn this way, SELECT DISTINCT acts on a subset of the table, and not on all of the data.
In the healthcare or academic fields, the operator is also very practical for group data from patients or authors who appear multiple times in different studies or articles, showing only one entry per entity for analysis purposes.
Managing duplicate references in bibliographic databases
In the field of scientific documentation, bibliographic databases usually offer specific tools to remove duplicate references When you conduct searches across different sources, this is crucial to prevent your literature reviews from being filled with duplicate articles.
In these systems, there is usually a "Remove duplicates" command within the tools menu, which It analyzes the result set and automatically removes duplicate references.The system usually reports how many elements have been deleted and how many remain in the current set.
On many platforms you can configure, from a preferences section, that The removal of duplicate references is done automatically. each time you perform a new search. This saves a lot of manual work, although it's advisable to regularly check that the duplicate criteria are correct.
In addition to bulk deletion, these managers allow you to manually select specific references to decide whether to keep or delete them. This manual review is useful when the system is unsure whether two records are actually the same item. or if they correspond to different versions (for example, preprints and final versions).
After removing duplicates, the result set is updated and shows the reduced number of referencesThis numerical control helps to validate that the debugging has had an effect and to document the process in systematic reviews or search reports.
Passionate writer about the world of bytes and technology in general. I love sharing my knowledge through writing, and that's what I'll do on this blog, show you all the most interesting things about gadgets, software, hardware, tech trends, and more. My goal is to help you navigate the digital world in a simple and entertaining way.