- The virtualization of hardware allows you to run several OS on a single physical machine through independent and protected environments.
- To enable virtualization it is essential to activate it in the BIOS or UEFI of the equipment, accessing advanced menus according to the manufacturer.
- So much Intel (VT-x) and AMD (AMD-V/SVM) offer specific technologies to optimize virtualization and are compatible with all major hypervisors.
If you've ever wanted to run multiple operating systems on your computer, test software in isolated environments, or simply get the most out of your hardware, you've probably heard of the virtualization. Today, this technology is not only available in large companies and data centers, but is also available to anyone with a modern PC. However, for everything to work properly, it is necessary Enable virtualization from the BIOS or UEFI from your computer, an option that is often disabled by default and can go unnoticed.
In this article we explain, clearly and with practical examples, How to check if virtualization is active, the steps to enable it in different BIOS/UEFI types, and some tips to get the most out of Intel and AMD's main virtualization technologies. It doesn't matter if you have an old laptop or a brand new computer with Windows 10 or 11: Here you'll learn everything you need to enable and configure virtualization, as well as why it's so important.
What is hardware virtualization and what is it used for?
La hardware virtualization allows a single physical computer to function as if it were several independent computers by using Virtual machines. It is based on the creation of isolated virtual environments where you can run different operating systems and applications, which is ideal for development, testing, security, or even running apps that only work on other systems. All of this is achieved thanks to a key component: the hypervisor, a software that manages the computer's resources and distributes them among virtual machines, ensuring that each one functions as if it were an independent computer.
In the past, virtualization was reserved for business environments or servers, but thanks to advances in Intel and AMD processors, it's now easy to take advantage of it at home as well. Its main advantages include:
- Resource Optimization: allows you to make maximum use of the CPU, memory and storage available, avoiding waste.
- Isolation of environments: What happens in a virtual machine doesn't affect the rest of the system; if a VM fails or becomes infected, your main computer remains intact.
- Flexibility: You can test systems, programs, or configurations without fear, since you can delete or restore the virtual machine at any time.
- Additional security: Ideal for testing unknown software or simulating attacks in controlled environments.
For all these reasons, virtualization is used in both businesses and homes, allowing everything from managing servers to creating virtual labs for learning or development.
Virtualization technologies by manufacturer
So much Intel , the AMD They offer proprietary technologies to facilitate hardware virtualization. Although the goals of both are similar, there are important differences you should be aware of:
Intel VT-x (VMX)
Most modern Intel processors, including Xeon, Core i3/i5/i7/i9 series and some specific Pentium and Celeron processors, integrate the technology. VT-xThis feature allows virtual machines to directly access processor hardware resources, as if they were native processes. Virtualization performance increases significantly, surpassing software virtualization. Additionally, VT-x can manage memory, graphics, and input/output devices, facilitating tasks such as migrating virtual machines between different physical machines, a useful feature in enterprise environments and data centers.
AMD-V (SVM Mode)
AMD processors with virtualization support include the technology V-AMD, Also known as SVM (Secure Virtual Machine)Its primary function is to separate and allocate physical resources to virtual machines to improve performance and compatibility. AMD-V integrates seamlessly with hypervisors such as Microsoft Hyper-V and supports a wide range of CPUs, from desktop models (Ryzen, Athlon) to professional models (Threadripper, EPYC).
Major hypervisors supporting hardware virtualization
Most popular virtualization programs leverage these technologies to achieve a optimal performance:
- VMware Workstation and VMware Player: They support Intel VT-x and AMD-V, although in many cases virtualization is disabled by default and requires activation in the BIOS/UEFI.
- Oracle infrastructures VirtualBox: Compatible with both technologies, it offers great flexibility and is completely free.
- Microsoft Hyper V: Included in Windows 10/11 Pro and Enterprise, it uses VT-x or AMD-V depending on the processor. In Home versions, it can be enabled through some advanced settings.
- KVM and Xen: widely used in Linux, taking advantage of hardware virtualization in recent kernel versions.
- Parallels: very popular in Mac, supports Intel VT-x and makes it easy to run Windows and other systems on Apple computers.
How do you know if your computer supports and has virtualization enabled?
Before configuring in the BIOS or UEFI, it is a good idea to check if your processor supports virtualization and if it is enabled:
- In Windows: open the Task Manager (Ctrl + Shift + Esc), select the tab Unlimited and search CPU. There, check if it appears Virtualization. If it says Enabled, you are ready; if it indicates Disabled, you must enable it from the BIOS/UEFI.
- Manufacturer's Tools: Intel and AMD offer free utilities to check compatibility. From their official websites, you can download and run these tools to verify if the VT-x or AMD-V option is available and active. To better understand how to enable virtualization from the BIOS or UEFI, we recommend visiting our Complete guide to accessing UEFI settings.
How to enable virtualization in traditional BIOS (Phoenix, AMI, etc.)
On computers with a classic BIOS, the process is simple but requires attention:
- Completely turn off the equipment.
- Turn it on and press the BIOS access key several times; normally Delete, F2, I, or in some cases F10 o F12.
- Within the BIOS, navigate using the arrow keys until you find menus such as Advanced, System Configuration o CPU Features.
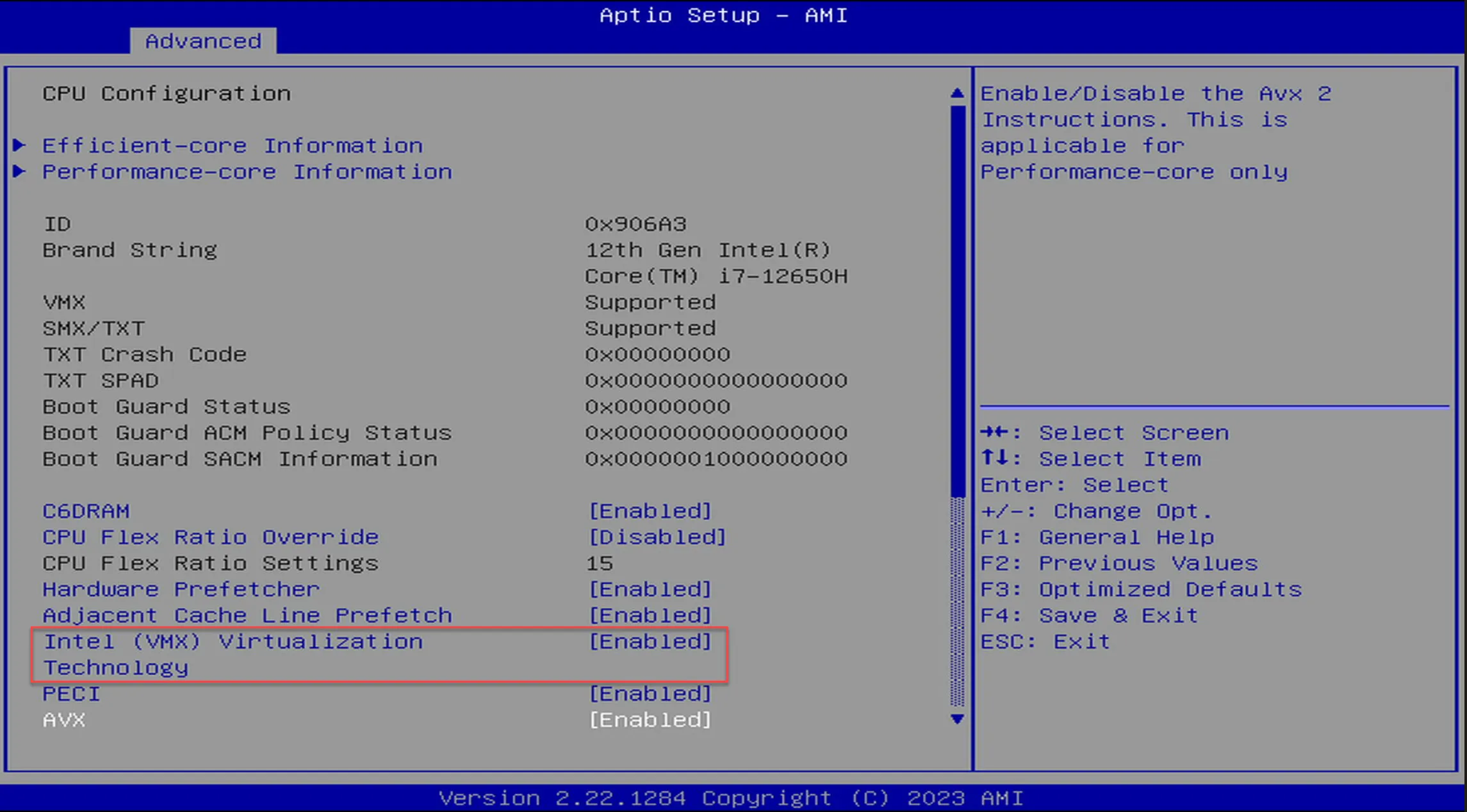
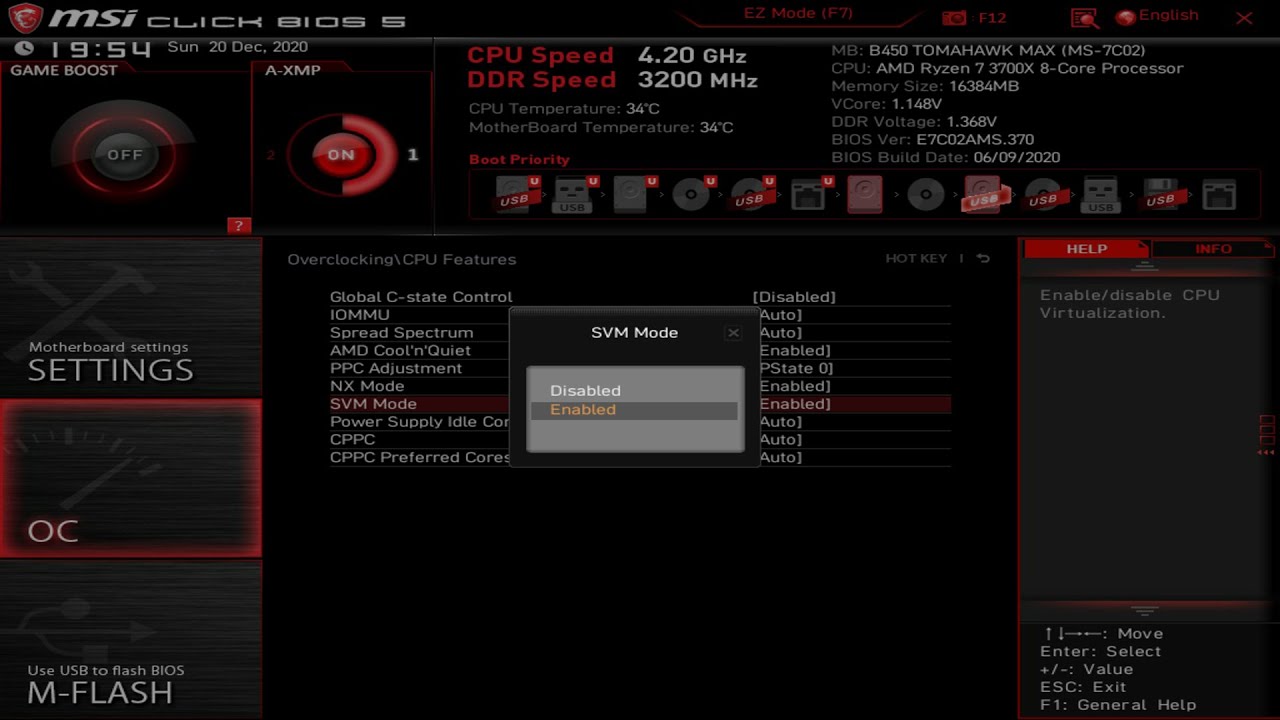
- Look for the option Intel Virtualization Technology, VT-x, AMD SVM o Virtualization Technology.
- If it appears in Disabled, change it to Enabled using Enter or the + and - keys.
- Save changes with F10 and restart.
On some computers, the name may vary slightly or the option may be hidden. If you have any questions, consult your motherboard's specific documentation or visit our dedicated section. How to know if your CPU is compatible with virtualization.
How to enable virtualization in BIOS UEFI (graphical interface)
Modern systems with graphical BIOS or UEFI make it easier to access and configure:
- From Windows 10/11, press and hold the key Shift and select Restart To access advanced options, then select Solve problems > Advanced > UEFI firmware settings, and finally Restart.
- Upon reboot, enter the UEFI and navigate to the menu Advanced, CPU Settings or similar.
- Look for the option Intel Virtualization Technology o AMD SVM Mode and change it to Enabled.
- Save changes and reboot from the UEFI menu.
Names may vary by manufacturer, but the important thing is to identify keywords such as 'Virtualization', 'VT-x', 'SVM' or 'Virtualization Technology'.
Enable Hyper-V and the Virtual Machine Platform in Windows
In Windows, in addition to enabling virtualization in BIOS/UEFI, you may need to enable some operating system features, such as Hyper-V and Virtual machine platform:
- From the Control panel or Windows search, go to Windows features.
- Brand Hyper-V y Virtual machine platform.
- Balance Accept and let Windows install the necessary components.
- Reboot to apply changes.
This is essential if you plan to use Hyper-V or need compatibility with other virtualization programs that require the operating system virtualization layer.
Additional recommendations and common problems
- If the virtual machine does not work correctly after enabling virtualization, check that there are no technologies blocking it, such as VT-d, security features (Secure Boot), or antivirus that may limit its use.
- In some portableThe lock may be at the BIOS/UEFI level and require a firmware update. Consult the manufacturer's website if you have any questions.
- Remember to carefully save changes to the BIOS/UEFI to avoid errors in the Boot after modifying the configuration.
- If you can't find the option in your BIOS, look in your computer or motherboard documentation, as names and locations may vary.
Once you understand how virtualization works and how to activate it, you can harness the full power of your computer to manage virtual machines more securely and efficiently. For more advanced virtual machine management, you may also be interested in learning about Creating and using checkpoints in Hyper-VAlthough the steps are similar across different motherboards and brands, menu names may vary. Don't hesitate to consult the manufacturer's website if you need specific help or want to verify your CPU's compatibility.
Passionate writer about the world of bytes and technology in general. I love sharing my knowledge through writing, and that's what I'll do on this blog, show you all the most interesting things about gadgets, software, hardware, tech trends, and more. My goal is to help you navigate the digital world in a simple and entertaining way.