- Set up your network and Private profile; enable discovery and sharing, and open SMB ports.
- Combine SMB permissions and NTFS with local users/groups for real control.
- Connect via UNC and map drive; supports clients Windows and Ubuntu with authentication.
- Avoid SMB1 and Guest; use SMB3 and apply solutions to common errors.
To collaborate without headaches in Windows 11, the essential is share folders and assign permissions correctly: this way each person sees, edits, or deletes only what they should. On small or home networks, it works with a couple of clicks, but if you want reliability, performance and safety, it is worth mastering SMB, NTFS, Users, Groups, and the Firewall.
In this guide we have gathered and rewritten, in a clear and orderly manner, everything you need: how to prepare the network, create local accounts, share with “Specific Users” or “Advanced Sharing”, adjust NTFS permissions, connect from other computers (even from Ubuntu), avoid repetitive passwords without losing security, when (not) to activate SMB 1.0 and how to solve typical errors like 0x80070035. Let's do it step by step, but keep an eye on the best practices.
Before you start: prepare your network and equipment

First make sure the connection is on Private network profile, as in Public Windows it limits visibility and sharing. In Windows 11, go to Start > Settings > Network & Internet, enter your adapter and select Private.
Activate the Private profile options Network discovery y File and printer sharingThis allows you to be found on the network and other computers to access your shared resources without unnecessary blocking.
If you're using the classic Control Panel: Control Panel > Network and Internet > Network and Sharing Center > Change advanced sharing settings. You can also open it with control /name Microsoft.NetworkAndSharingCenter or go directly to the advanced page with control.exe /name Microsoft.NetworkAndSharingCenter /page Advanced.
Check your firewall: Windows should allow SMB. At the network level, make sure TCP ports are open. 445, 139, 138 and 137. Without this, the best tutorial won't save you. Repeat these settings on the server computer (where you share the folder) and on the client (from where you connect).
Quick concepts: a SMB server is the team that shares the folder; a SMB client is the one that connects. They can be in the same workgroup, outside the domain, and in the same subnet to simplify discovery.
Creating local users and groups: the basis for well-controlled access

Don't give up your personal account so others can access your resources. Professionalism is the key. create specific local accounts and if several people need to have the same level of access, group them into a local group.
Open the Computer Management console from the context menu of This PC > Manage (or run compmgmt.msc). Inside, go to Local Users and Groups > Users and create new users with “New User”.
Set a name and password and review the account options. By default, they join the group. Users, which is a good place to start. You can create users like “user11,” “user12,” etc., to assign them granular permissions later.
To share with common permissions, create a local group: In Local Users and Groups > Groups > New Group. For example, “sharegroup1”. Click Add, write users and use Check names to validate that they exist. So, by giving permissions to the group, you give them to all members at once.
Sharing folders: quick method and advanced sharing
For a shortcut from Explorer, right-click the file or folder and choose Grant access to > Specific users. Or select the item, open the tab Share and, under “Share with,” choose “Specific users.”
Select a specific person or choose All for general network access (not recommended without limits), and set its level (Read or Read/Write). If you select multiple files or a folder, are shared in blocks; everything inside a shared folder inherits access.
If you want fine control (and it is recommended), use Advanced sharingRight-click the folder > Properties > Sharing tab > Advanced Sharing > select “Share this folder.” Assign a share name (e.g., “share01”).
Balance Permissions. By default, “All” is read. The professional pattern is remove “All”, press Add and select the exact group or users (for example, “sharegroup1” with Full Control and “user14” with Read only). This way, you can limit who can log in and to what extent.
Tip: You can manage resources from the plugin. Shared folders running fsmgmt.msc (or in Computer Management > System Tools > Shared Folders). Used to create, review open sessions, and view files in use or disable shared resources.
NTFS Permissions (Security) and SMB Permissions: How They Work Together
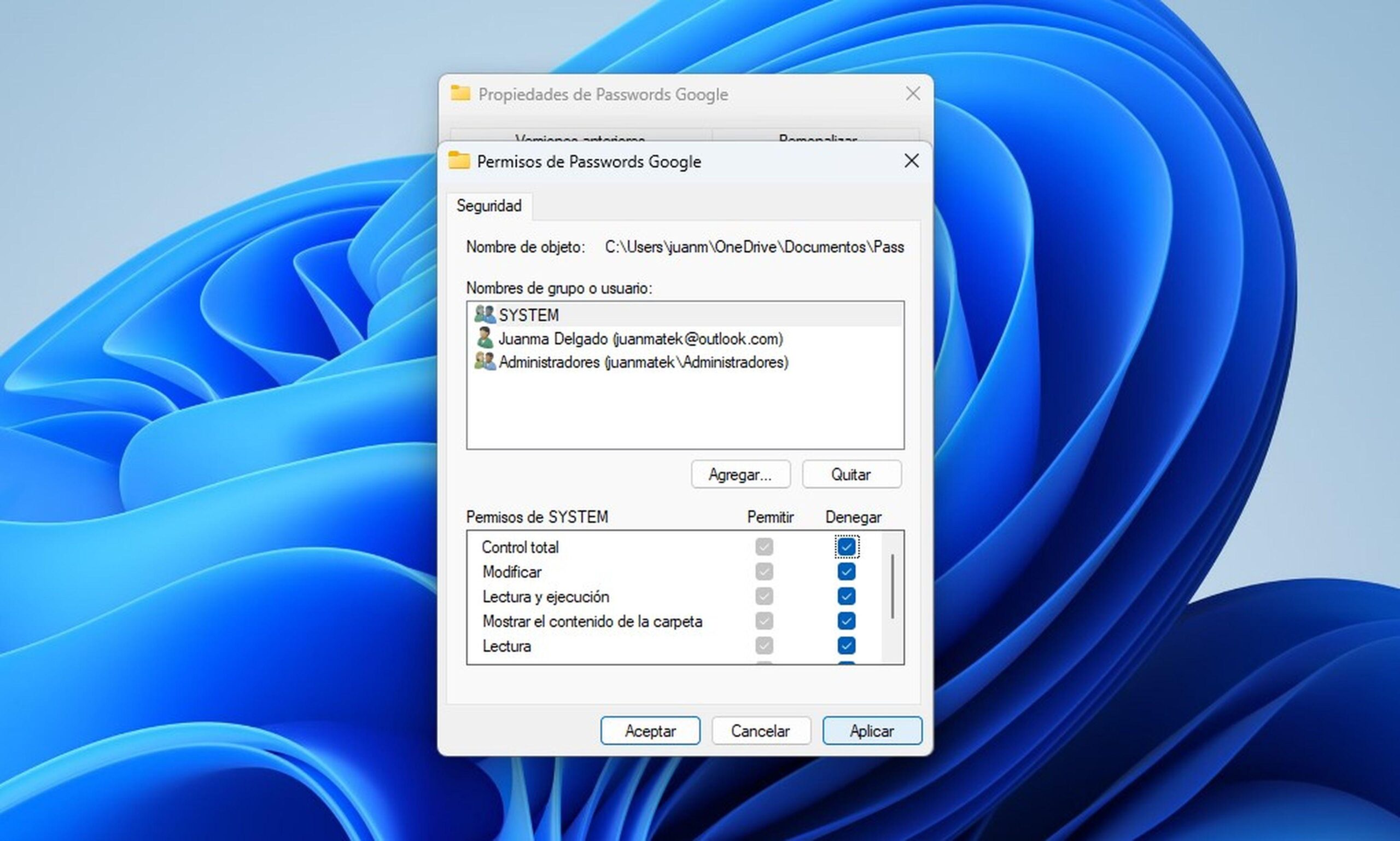
After setting up sharing (SMB level permissions), it's time to review the Security tab of the folder (NTFS permissions). Go back to Properties > Security > Edit > Add, and add the same groups/users (e.g., “sharegroup1” and “user14”).
Assign Full Control who should manage and permissions Reading to whomever needs to be consulted, consistent with what you put in “Share”. Remember: effective access is the intersection of both worlds; if you give Full Control in SMB but only Read Control in NTFS, Read will win.
When you close, you'll see the final list of entries and the network path of the shared resource under Security. If the computer name fails, you can use the IP address. For example, the UNC path would be \\Computer10\\share01 o \\192.168.101.212\\share01.
Alternatively, there is “simple sharing” (Share button). It is convenient, but has fewer optionsAdvanced mode gives you clarity, scalability, and reduces permissions surprises.
Connect from other computers (Windows and Ubuntu) and map drive
In Windows, open Explorer and use the panel Red to discover teams. If you want to get straight to the point, type the following path into the address bar: \\ 192.168.101.212 o \\Computer10, or the full UNC path \\Computer10\\share01.
If you need to have it “always at hand”, assign a network driveRight-click the shared folder > Map network drive > select a letter and select “Reconnect at logon.” It will remain in place until you unmap it.
In Ubuntu, open Files > other locations, and in “Connect to server” write smb://computer_IP (for example, smb://192.168.1.97). Enter a valid username and password; you can leave the workgroup as default.
You can indicate whether Ubuntu should forget the password on exit, remember it until you log out, or remember it forever. When listing Windows resources, you'll see "normal" shares and administrative such as C$ or ADMIN$ (accessible only with administrator privileges). Ubuntu usually displays them, although in Windows they are hidden with a “$”.
Access without asking for a password every time: recommended method and risks of unprotecting
There is a surefire way to avoid typing your password every time you log in: use the same account (name and password) on the server and the client. If “User1” with “Password1” exists on both and you log in from the client as “User1”, the connection is authentic alone.
Avoid disabling the password-protected sharing. While you can do this in Advanced Settings > All Networks, and also enable “Share so anyone with network access can read and write to Public,” it is a bad security idea even in “trusted” environments.
There is a policy that allows you to apply “Everyone” permissions to anonymous users: Policy Editor (gpedit.msc) > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Local Policies > Security Options > Network Access: Allow Everyone permissions to apply to anonymous users. Enabling it opens the door to unauthenticated access.
About the integrated account Guest: It's disabled by default. Starting with Windows 10 build 10159, the classic Guest account can't be enabled or recreated. Force anonymous or guest access. greatly increases the attack surface.
SMB 1.0/2/3: Check versions, enable only when appropriate, and understand the risks
Windows 10/11 uses SMB 3.x by default. If you connect to older computers (like Windows XP) you may experience issues because they require SMB1.0, disabled for security. Check versions with PowerShell:
- SMB 1.0 on Windows 10/8.1:
Get-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName SMB1ProtocoloDism /online /Get-Features /format:table | find "SMB1Protocol" - SMB 2 on Windows 10/8.1:
Get-SmbServerConfiguration | Select EnableSMB2Protocol - Windows 7:
Get-Item HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters | ForEach-Object {Get-ItemProperty $_.pspath} - View SMB1 and SMB2 at once:
Get-SmbServerConfiguration | select "*enablesmb*"
To enable SMB 1.0 support (only if you really need it): Control Panel > Programs and Features > Turn Windows features on or off > check Support for SMB 1.0/CIFS file sharing. Please note that Windows may uninstall SMB 1.0 automatically if not used within 15 days (since version 1709).
You can also use PowerShell and other tools: Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName SMB1Protocol, Set-SmbServerConfiguration -sEnableSMB1Protocol $true, Install-WindowsFeature FS-SMB1, customer only: Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName "SMB1Protocol-Client" -All, server only: Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName "SMB1Protocol-Server" -All.
Disable SMB 2 only exceptionally (and understand the impact): reg.exe add "HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\LanmanServer\Parameters" /v "SMB2" /t REG_DWORD /d "0" /f; sc.exe config lanmanworkstation depend= bowser/mrxsmb10/nsi; sc.exe config mrxsmb20 start=disabled. To revert, go back to enable SMB2 to Set-SmbServerConfiguration -EnableSMB2Protocol $true.
Eye on security: campaigns like WannaCry or NotPetya exploited SMBv1 vulnerabilities (EternalBlue, etc.). If you don't need SMB 1.0, don't activate it. Prioritize SMB 3.x whenever possible.
Permissions and Public Folders in Outlook: A Helpful Reference of Levels
In environments where they are also managed public folders (as in Outlook), you'll see predefined permission levels: from Owners (all) to In collaboration with: (minimum). When customizing boxes, the “Permission Level” changes to Personalized.
The typical flow: right-click on the public folder > Properties > tab Permissions > choose level, adjust, and with Add Add users or groups from the global notebook. Repeat for different groups and close with Accept.
This layered logic helps to understand, by analogy, how to scale granular permissions also in NTFS/SMB when you plan access by roles and groups.
Troubleshooting: Typical Errors and How to Get Out of a Jam
If you see “Windows cannot access \\hostname\\share” or “You don’t have permission…”, check that the user/group is really added in the permissions of Share and tab Security (NTFS).
PowerShell Tools: Get-SmbShareAccess -Name "share01" to view SMB permissions of the resource, and get-acl C:\\share01\\ | fl to list the NTFS ACL. Make sure to use your actual resource name and path.
If there are doubts with credentials, clean old entries in the Credential manager (Control Panel > User Accounts > Credential Manager) or open the classic manager with rundll32.exe keymgr.dll,KRShowKeyMgr.
Check services: they must be active on the file server.Publishing resources for feature discovery"And"Feature Discovery Provider Host", and in general the service employee. It can also be key “TCP / IP NetBIOS Helper".
Error 0x80070035 (Network path not found): This usually indicates an SMB incompatibility or blockage. Check the versions (SMB1/2/3) and that the firewall and the aforementioned services are working. If you insist on guest access (not recommended), there is the “Enable insecure guest logins"In Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Network > Lanman Workstation and the registration adjustment reg add HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanWorkstation\Parameters /v AllowInsecureGuestAuth /t reg_dword /d 00000001 /f.
If a warning appears when reconnecting a unit of type “Policies block unauthenticated guest access", is the behavior since Windows 10 1709: Unsigned SMB v1/v2 is insecure. The good solution is to use SMB v3 and authenticated connections.
Error 0 x 80004005: can jump when SMB1.0 is disabled and the other end only speaks SMB1. Review the SMB section and consider secure alternatives (ideally, upgrade or reconfigure for SMB 3.x).
Connection Limits: On Windows client (7/10/11) there is a maximum of 20 simultaneous connections to the shared resource. For scenarios with many users, mount the service on Windows Server or on a prepared NAS.
To share quickly and securely in Windows 11, prepare your network well (Private profile, active discovery and sharing), create dedicated users and groups, use advanced sharing and align SMB permissions with NTFS; connect via UNC, map drives if convenient, avoid the guest and only resort to SMB 1.0 when there is no other option, relying on checks and Tricks problem solving to save time when something is unresponsive.
Passionate writer about the world of bytes and technology in general. I love sharing my knowledge through writing, and that's what I'll do on this blog, show you all the most interesting things about gadgets, software, hardware, tech trends, and more. My goal is to help you navigate the digital world in a simple and entertaining way.