- OneDrive and SharePoint They automatically maintain a version history, including major, minor, and log versions for critical documents.
- It is possible to restore previous versions and even the entire OneDrive from the web, File Explorer, or the Office 365 applications themselves.
- There are version limits, retention times, and risks of accounts being frozen due to space or inactivity, which should be understood and managed.
- Combining version history, recycle bin, and good naming practices improves document security and traceability.
In everyday life with Microsoft 365, working with documents WordExcel, PowerPoint, and files shared on OneDrive or SharePoint It's perfectly normal. But when several people are editing at the same time, or when we need to recover a previous version, things can get complicated if we don't know how version control and change tracking work in the Microsoft cloud.
If you've ever found yourself surrounded by files like this “final_definitive_presentation_v3_good_now_yes.pptx”This article is for you. We'll take a detailed look at how version control works in OneDrive and SharePoint, what logs are in information management, and how to recover previous versions (from the web, from File Explorer, and from the system itself). apps (from Office), how to restore your entire OneDrive to a previous point and what limits and retention times Microsoft 365 handles.
What is version control in Office, OneDrive, and SharePoint?
In the Microsoft 365 ecosystem, Version control is the ability to automatically save different "states" of the same file as it is modified. This version history is integrated into OneDrive and SharePoint and works with virtually any type of file: Office documents, PDFCAD files, photos, videos and much more.
Unlike manually saving many files with different names, The version history maintains a single file with multiple internal versions.which you can consult and restore when needed. This system is complemented by retention labels and the concept of records in SharePoint Online and OneDrive for Business, designed for compliance and records management scenarios.
In organizations that use SharePoint intensively, In addition to the standard version history, there may be what is called "registry version control"., which adds a special layer of protection and traceability to certain documents that must be treated as official records (contracts, internal policies, legal documentation, etc.).
On the other hand, in many SharePoint libraries A distinction is made between major (larger) versions and minor (smaller) versions.Major versions (1.0, 2.0, 3.0…) are typically used for important milestones, such as when a document is released for general review, while minor versions (1.1, 1.2, 1.3…) are used while the file is under development.
Organizations typically configure draft security so that Only the file owner and people with approval permissions can see minor versions.so the rest of the team only sees the major, already "official" versions. In SharePoint lists, only major versions are tracked, and these are always numbered with integers.
Version control of records in SharePoint Online and OneDrive
In compliance and advanced document management scenarios, It is common to need certain documents to be considered official “records”.with clear restrictions on what can be done with them (for example, that they cannot be deleted or modified while locked). Even so, it is often necessary to continue working and generating new versions from those records.
Imagine a sales contract: You can mark the signed version as a record to ensure it remains intact, but perhaps some clauses need to be updated later. In that case, a later version is generated, which can also be marked as a new record, always keeping the previous versions that were already registered accessible.
SharePoint Online and OneDrive for Business enable precisely this through the function of record version controlOneNote notebook folders are the big exception: in that specific case, they do not support this type of record version control.
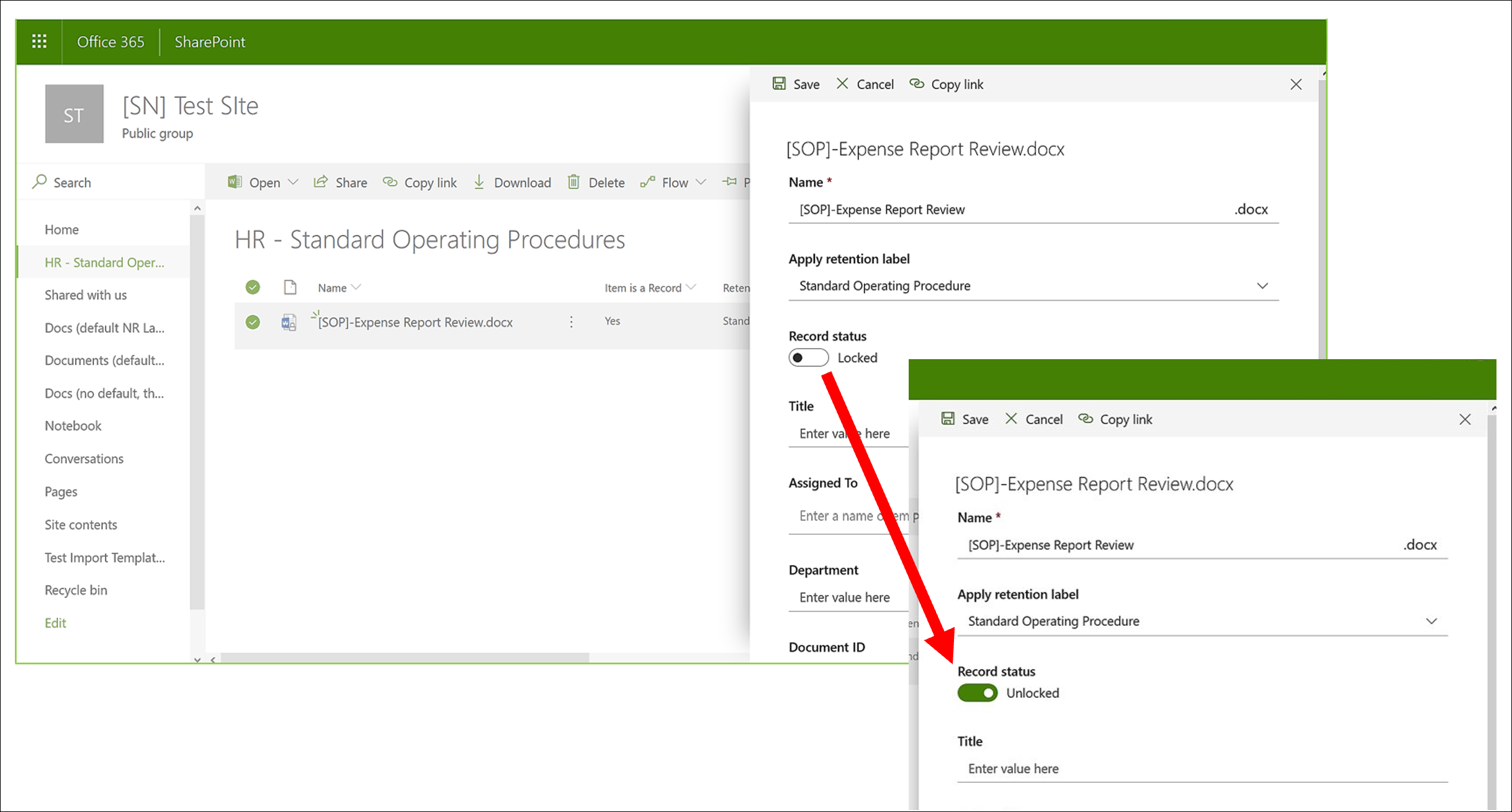
To use it, you first need to Apply to the document a retention label configured to mark the content as a recordFrom that point on, a document property called “Record Status” appears, displayed next to the retention label itself. Depending on how the label was configured, the initial status of the record can be “Locked” or “Unlocked.”
With this active configuration, you may:
- Edit the document and generate individual versions as recordsThe system alternates the "Record Status" between locked and unlocked. A new version is only kept as a record when the status is "Locked," reducing the risk of accumulating unnecessary copies.
- Have log versions automatically stored in a local repository associated with the siteEvery SharePoint and OneDrive site has a preservation suspension library, and within it is a "Logs" folder where these versions are stored as separate files.
- Maintain a "living" document that keeps the entire version historyIn document libraries, from an item's menu you can consult the version history at any time, seeing at a glance which are registered versions and opening those copies when needed.
If the retention label is set to require a disposal review at the end of the retention periodEach log version is evaluated independently. This allows you to decide what to do with each one individually, instead of treating the entire history as a single unit.
Default, Record version control is automatically activated on any document A record is assigned a retention tag that marks it as a record and is published on the site. From the document details panel, any user with appropriate permissions can change the record's status from "Locked" to "Unlocked" and vice versa. A padlock icon is also typically displayed to visually indicate when the file is locked.
As long as the document is unlocked, Any user with standard editing permissions can modify the fileHowever, it cannot be deleted, as it is still considered a record. Once editing is complete, the status is changed back to "Locked" to prevent further modifications until it is unlocked again.
Locking and unlocking records: what happens internally
When a retention label is applied that marks a file as a record, Any user with contribution permissions (or lower) can change the registration status From locked to unlocked and vice versa. The internal behavior is very specific and it's important to understand it to know what's happening with the files.
Unlocking a record triggers several automated actions:
- If the site does not already have a preservation suspension library, one is created at that time. automatically.
- Within that library, if the "Records" folder does not exist, it is also created to store registry versions.
- A "Copy to" action is executed, which copies the latest version of the document to the Records folder.Only the most recent version at that time is copied, not the entire history. The filename in that folder usually follows the format .
- The copy that goes to the Logs folder is linked to the version history of the original document., and in the comments field of that version the word “Record” is indicated.
- The original file becomes a new editable versionbut without the possibility of deletion. The "Item is a record" column in the document library continues to show "Yes", reflecting that the document retains its record status even though it can be modified.
When it returns to To block the record, the original document becomes uneditable.The important thing to understand is that the copy in the Logs folder is created when you unlock, not when you lock. Each unlock generates a new log version in the suspension library for preservation.
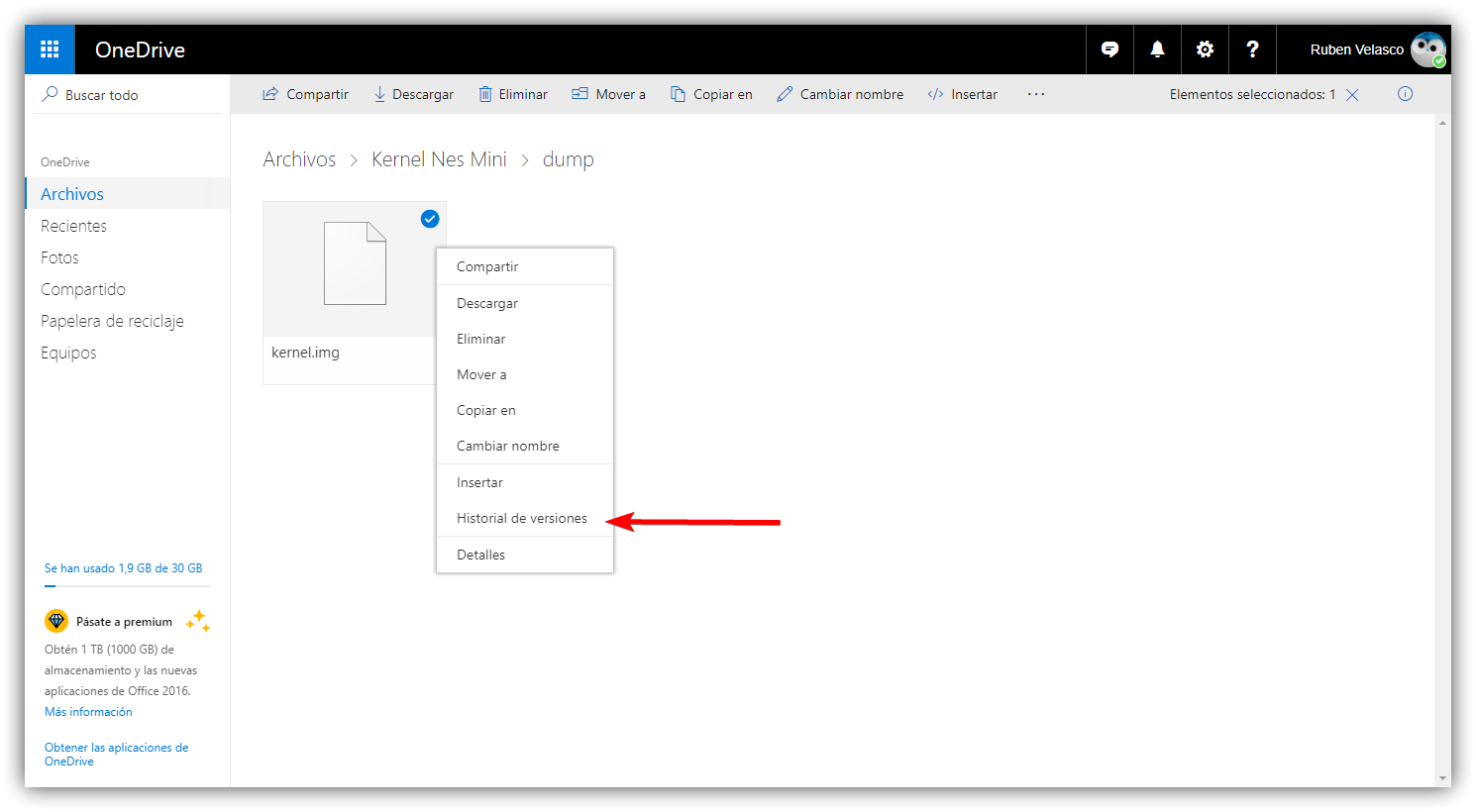
To view the different registration versions, simply Select the document in the library and use the “Version History” option. in the item's menu. From there you can see all versions, including those marked as "Record" in the comments field, and you can open each one if necessary.
The blocking and unlocking actions remain recorded in the Microsoft 365 audit logIn the “File and Page Activity” reports, you can filter events such as “Record status changed to locked” or “Record status changed to unlocked,” which facilitates compliance checks and internal reviews.
Practical use of version history in OneDrive and SharePoint
From the user's point of view, The most common reason is simply to want to recover a previous version of a file This is because content has been accidentally deleted, unwanted changes have been made, or the file has become corrupted. That's what OneDrive and SharePoint version history is for, both on the web and in File Explorer, as well as within the Office applications themselves.
In OneDrive (personal or professional), the basic process from the web is very straightforward: You log in, locate the file, right-click and choose “Version History”This opens a panel listing the different versions of the file with the modification date, who modified it, and the file size.
If you use a Microsoft 365 corporate or educational account, In the history panel you will see options with ellipses (...) next to each versionFrom there, you can select "Restore" to make that version the current one. The previous current version doesn't disappear; it simply moves to a previous version in the history.
In classic view or older versions of SharePoint Server, The restoration is done from a drop-down arrow next to the version numberThere you will also see the "Restore" option. The result is the same: the selected version becomes the current version of the file.
Note that You can only restore one file at a time.There is currently no native function to restore multiple versions of multiple files at once from the standard version history.
Version history from File Explorer (sync client)
If you use the OneDrive sync app on your PC with Windows, You also have access to the version history directly from File Explorer.which is very convenient if you work more from the desktop environment than from the web interface.
The procedure is simple: Open the OneDrive folder in Explorer, locate the file you want to recoverRight-click on it and select “Version History”. This will open a window listing the different versions of the file stored in the cloud.
From that list, Choose the specific version you want to restore, tap the three dots (...) and select "Restore"Just like in the web interface, the version you restore becomes the current one, and the one that was current just before the restoration becomes an older version, so you don't lose anything.
It is important to know that, again, You cannot restore multiple versions of multiple files at the same time using this Explorer function. Each restore is done individually.
Microsoft also documents in more detail how to use version history and It also explains how to locate lost files or files that appear to have disappeared. from OneDrive, something that sometimes happens when folders are moved or the synchronization path is changed.
Restore versions from Office 365 applications (Word, Excel, PowerPoint)
When you open a OneDrive document in Word Online, Excel Online, or PowerPoint Online, You can also access the version history from within the application itself.This is very useful for reviewing changes with visual context, seeing exactly what has been modified, and deciding which version you want to revert to.
To do this, open the file in the corresponding app (for example a .docx file in Word Online or an .xlsx file in Excel Online) and go to the menu “File > Info > Version History”. A side panel will open showing the different available versions.
When selecting a version of the panel, You can see it in the main window with the changes highlighted.From there, you'll usually have two options: "Save a copy" (to keep both versions) or "Restore," which makes that version the current one. The "Restore" button isn't shown for the latest version, as it's already the current one.
This approach is especially practical in collaborative environments, because it allows you to browse through the history, seeing who made each change and when.and decide if you want to keep an older version without having to leave the application.
Restore all of OneDrive to a previous point
In addition to restoring individual files, OneDrive for Business offers a very powerful feature: restore your entire OneDrive to a previous stateThis is especially useful in cases of massive file corruption, accidental deletion of many documents, or attacks. malware (for example, ransomware).
To use this option, access OneDrive from your browser, Click on the “Settings” icon in the top right and select “Restore your OneDrive”A specific page will open for this function.
On that page, You can choose a date to which you want your OneDrive status to revert., with quick options like “Yesterday”, “A week ago”, “Three weeks ago” or a custom date and time.
The interface displays a graph showing the activity of changes to your files over time and a slider for visually mark the point in time you want to return to.Below, you will see a detailed list of the changes (files modified, deleted, or restored), indicating who performed each action and at what time.
Select the changes you want to revert or the time period you're interested in, and once you're clear on that, Click on the “Restore” buttonThe system will undo those changes and return your OneDrive to its selected state. It's a kind of "time machine" for your entire storage space. storage.
Recover deleted files from the recycle bin
When you delete a file from OneDrive, That file is also deleted from the other synchronized devices.Because synchronization maintains the same state in the cloud and on local computers, if you accidentally delete something, you usually won't find it on any other synchronized computer either.
The good news is that, as long as the bin hasn't been emptied and nothing has happened There retention, Deleted files can be recovered from the OneDrive recycle bin on the webTo do this, go to OneDrive in your browser and, in the left panel, click on “Recycle Bin”.
You will see a list of the deleted items, including Information such as the deletion date, the name of the user who deleted them, and the original locationSimply select the files and folders you want to recover and click the "Restore" button. The items will be returned to their original location, provided it still exists.
This recycling bin is also subject to a maximum retention periodTherefore, files are not stored there indefinitely. It's important to be aware of these limits, especially in corporate environments.
Version limits and retention periods in OneDrive and Office 365
In personal OneDrive accounts, Older versions of a file are kept for 30 daysWithin that period, you can retrieve up to 25 versions of each file. After that time, older versions may be deleted according to the retention policy.
In the case of Microsoft 365 accounts for organizations, The number of stored versions and the exact behavior depend on the library configuration. defined by the administrator. There is no single universal value, as each company can adjust these options according to its needs and storage policy.
Regarding the removed items, The standard maximum period for keeping files in the SharePoint and OneDrive for Business recycle bins is 93 days.That limit can be reduced, but not extended beyond it, and administrators can adjust it below 93 days. In any case, deleted items are always retained for a minimum of three days.
In libraries that use major and minor versions, there are also other limitations: The maximum number of minor versions that can be accumulated for each major version is 511The maximum number of major versions is configurable. If you attempt to save another minor version beyond this limit using modern clients, the most recent minor version will be overwritten.
However, if an older client is being used and the maximum number of minor versions is reached, It will not be possible to save or load changes until a new major version is released.Once published, space is available for up to 511 new minor versions associated with that main version.
Managing frozen OneDrive space and accounts
When the OneDrive storage limit is exceeded, The account may be "frozen" and switched to read-only mode.In that state, although you can log in, it will not be possible to continue uploading files or synchronizing new changes from devices.
There are two basic ways to resolve this situation. The first is Purchase more storage space by upgrading to a higher subscription planAfter payment, the upgrade may take up to 24 hours to be applied and unfreeze the account.
The second option is Delete files to free up spaceFrom the OneDrive web interface, you can sign in and choose "Unfreeze your account to temporarily access your files." For a period of 30 days, your files will be in read-only mode, giving you time to delete any you no longer need.
Within that timeframe, You can download important documents to your local drive and then delete them from the cloud. To reduce storage space usage. If you don't clean up enough within those 30 days, the account will be frozen again and the temporary unfreezing option will no longer appear. At that point, your only option is to contact Microsoft support.
Another relevant aspect is inactivity: if you do not access your OneDrive account within one yearYour account may be frozen even if you continue using other Microsoft 365 services. To avoid this, it's advisable to log in to the OneDrive web interface at least once a year or maintain some activity with the desktop client.
Best practices for naming and organizing versions
Although version history greatly simplifies management, many people still manually naming the documents with numbers and dates to maintain some visual control over versions. This system can coexist with the history, provided it is used in an organized manner.
A common practice is Add the date to the beginning of the name in year-month-day format. (for example, 230107 for January 7, 2023) and then a numeric suffix to indicate the significance of the change. For example: “230107_memory_1” for a first major version of a project memo.
While minor changes are being made, Sublevels of type 1.1, 1.2, 1.3 can be addedso that they end up with names like “230107_memory_1.1”, “230108_memory_1.2”, etc. This indicates that they are incremental adjustments on the same main milestone.
When a thorough review takes place, for example following a review by a supervisor, The main number can be changed and rename the file as “230131_memoria_2”, making it clear that there is a significant leap from the previous series of drafts.
However, it is worth remembering that True fine-tuning is offered by the version history of OneDrive and SharePointespecially when combined with the ability to see which user made which changes and when, and with retention and registration labels for documents that require legal traceability.
Comments, commits, and Git-style alternatives
One point that many users, especially those from the software development world, miss is the ability to add clear and structured "commit" messages to each versionas is done in Git. OneDrive automatically preserves versions, but it doesn't always allow you to document in detail what has changed between versions.
In corporate environments that use SharePoint, There are options such as change control and commentsapproval workflows and use of master versions for milestones which help to approach this type of control. It's not Git as such, but it does provide more context than a simple list of dates and authors.
If you don't have permission to configure SharePoint or modify libraries (common in work accounts), You may be limited to the standard OneDrive options.In such cases, the combination of a good naming system, the disciplined use of major/minor versions in libraries where enabled, and the habit of reviewing the history before major changes can make all the difference.
For more advanced needs, such as retaining versions for longer periods, having additional external copies or having even more detailed control over the file lifecycleMany organizations opt for specialized backup solutions that also include OneDrive and other Microsoft 365 data within their protection strategy.
This entire set of features—version history, logs, recycle bin, full OneDrive restore, space control, and naming best practices—forms a A fairly powerful toolbox for preventing data loss and working more securely with Office and OneDriveprovided it is well understood and used judiciously.
Passionate writer about the world of bytes and technology in general. I love sharing my knowledge through writing, and that's what I'll do on this blog, show you all the most interesting things about gadgets, software, hardware, tech trends, and more. My goal is to help you navigate the digital world in a simple and entertaining way.