- Power Pivot allows you to create advanced relational models in Excel
- Import large volumes of data from multiple sources easily
- Automate advanced analysis and custom calculations with DAX
Wondering how to get the most out of your data in Excel and take your analysis to the next level? If you work with information, whether in business or academia, you've probably felt that traditional Excel tables and functions aren't enough. Fortunately, PowerPivot is here to revolutionize the way you manage large amounts of data, creating advanced models and generating dynamic reports in an agile and hassle-free way.
In this article, you'll find a comprehensive guide to data models in Excel using Power Pivot. You'll discover what makes it so special, how it differs from traditional tools, how to import data, create relationships, and get the most out of it with DAX functions. All explained in a user-friendly language, with practical examples, so you can start from scratch or perfect your skills if you already have experience.
What is Power Pivot and why is it revolutionizing Excel analysis?
Power Pivot is an advanced Excel add-in designed to facilitate complex data analysis and modeling. With this tool you can import massive amounts of information from different sources, combine them, establish relationships between tables and perform highly advanced calculations, far beyond what conventional tables and formulas allow. What's really cool is that all of this happens within the familiar Excel interface, without having to learn completely new programs.
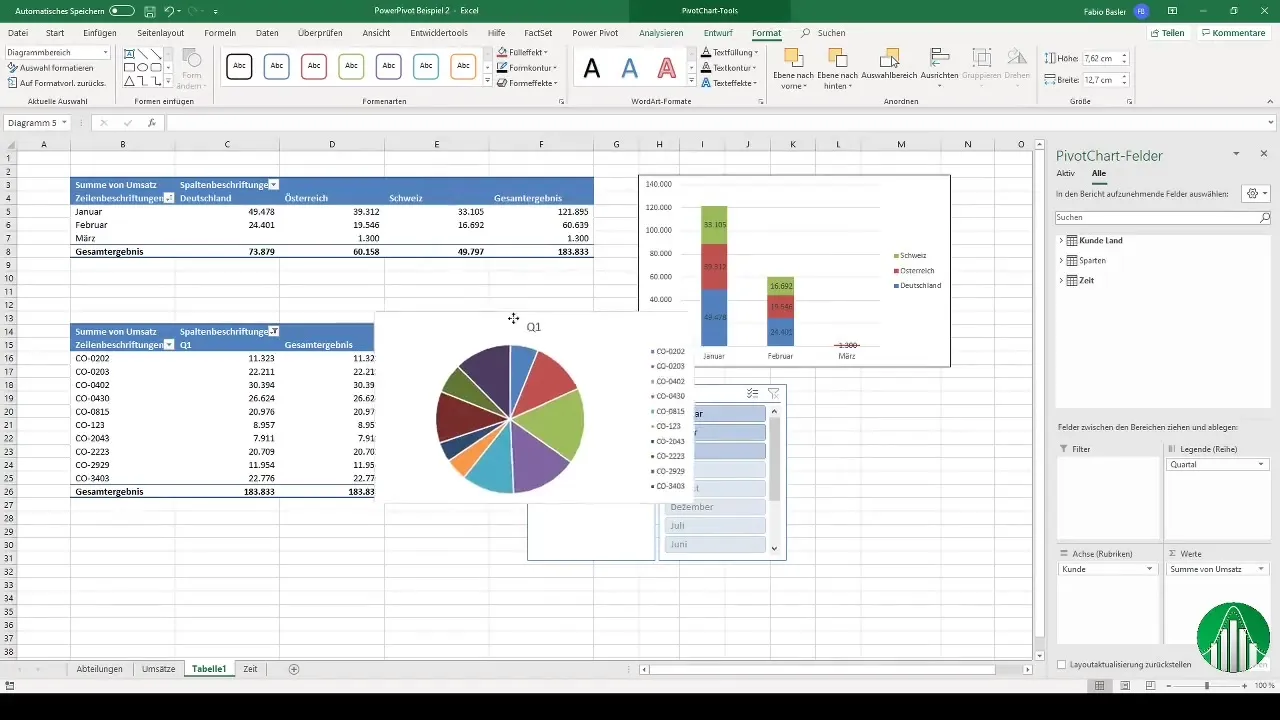
One of its great strengths is the ability to create relational models directly within your Excel workbook. Imagine having a relational database like Access, but fully integrated and managed from your regular spreadsheet. These models are also the basis for building much more powerful and flexible pivot tables and charts.
Advantages of working with data models and Power Pivot
Using Power Pivot on a daily basis means taking a giant leap forward in your productivity and analytical skills. These are the advantages that stand out most among users and experts:
- Handling large volumes of dataWhile classic PivotTables are limited by the number of rows Excel can process, Power Pivot leverages an in-memory processing engine capable of handling millions of records without slowing down the application.
- Combine data from multiple sources: You can not only analyze data from a spreadsheet, but also import from databases SQL, Access, text files, cloud services, web pages, and more—all in a single, integrated model.
- Advanced relational model: Establish relationships between different tables, as if you were building a database. This allows you to cross-reference information from different sources without duplicating it and perform much more sophisticated analyses.
- Automatic and custom calculations: Using DAX (Data Analysis Expressions), you can create calculated measures and columns with operations that go far beyond traditional formulas, automating custom metrics and advanced analysis.
- Ease of use and full integration with Excel: All work is done from the standard interface you're already familiar with, so you don't need to switch software or learn new environments.
How is information stored in Power Pivot?
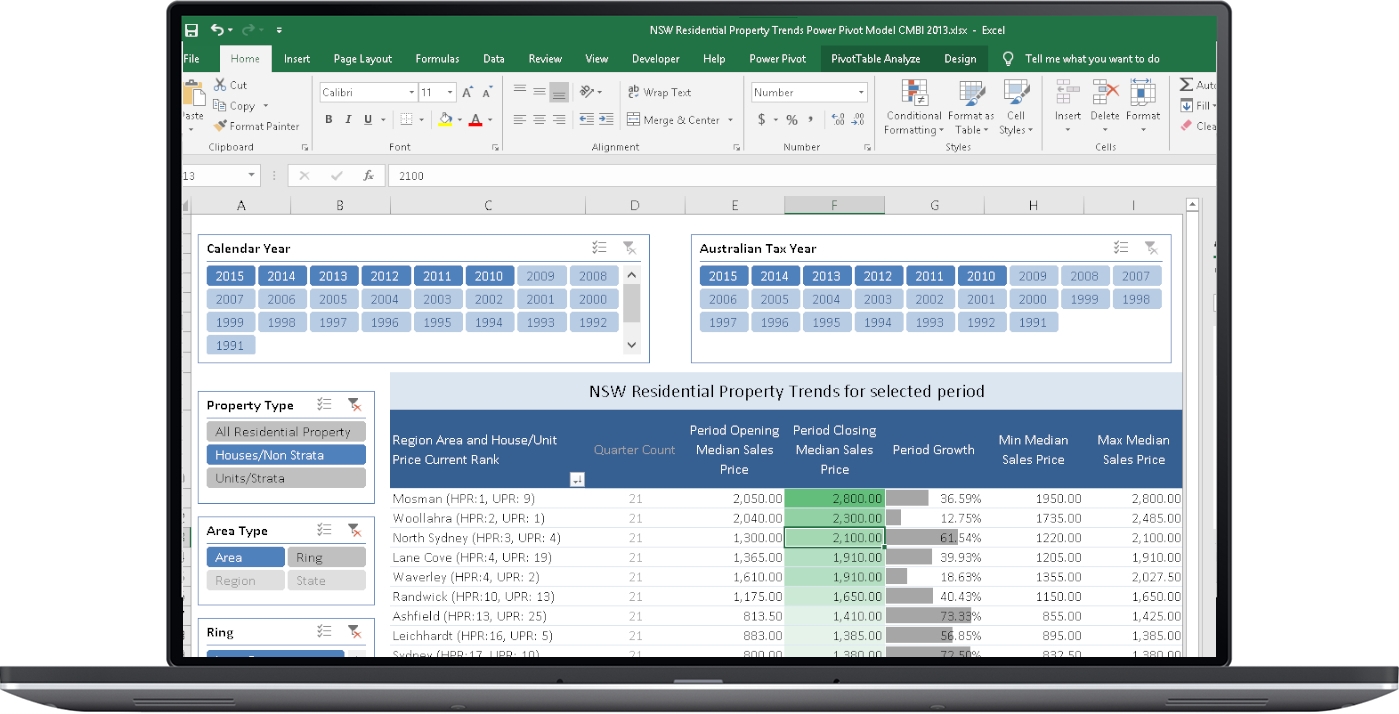
When you use data models in Excel with Power Pivot, all the information is stored in an analytical database within the Excel workbook itself. This proprietary structure, managed by a powerful analysis engine, allows data to always be available for use in pivot tables, charts, and other visualization tools without delay. Furthermore, files can grow up to 2 GB and be loaded into memory up to 4 GB, significantly reducing Excel's physical limitations.
Another advantage is the full integration with Excel's presentation functions. You can work with slicers, filters, and custom formulas using your data models, all in a single, shareable, and easy-to-maintain file.
Step-by-step guide to creating data models in Excel with Power Pivot
1. Import data from multiple sources
The first step in data modeling is to import information from the sources you need. In recent versions such as Excel 2016 and those included in Microsoft 365, simply go to the 'Data' tab and select 'Get & Transform Data' to import from text files, Excel workbooks, websites, Access databases, SQL Server, and many more relational sources.
- You can select one or more tables when importing data. If you select the option for multiple tables, Excel will automatically create a data model and add all of them.
- If you need to adjust the information before importing it, use the query editing option to cleanse and transform the data before loading it into the model.
2. Add data to an existing model
You can always add new tables or ranges to your data model, even if you're already working in it. For that:
- Select any range of data in your spreadsheet. It's recommended to convert it to an Excel table for greater flexibility.
- Click 'Power Pivot' > 'Add to Data Model' to include that table in your model.
- You can also insert a pivot table and check the box to add that data to the data model.
In this way, the range or table is directly linked to the data model, allowing the information to be automatically updated whenever the source data is modified.
3. Create relationships between tables
The great difference in data modeling lies in the relationships between tables. To create them, it is essential that each one has at least one key (unique) field, such as the client, student, product identifier, etc.:
- On the 'Power Pivot' tab, go to 'Manage' and select 'Diagram View'.
- All imported tables will be displayed. You can reorder and resize them to better view their fields.
- To create a relationship, simply drag a key field from one table (e.g., Product ID) onto a corresponding field in another related table (e.g., Sales or Stock).
- The lines that appear represent the links already established, facilitating the exploration of the data.
This way, you can cross-reference information between different tables without duplicating data, replicating the structure of a relational database and facilitating complex analyses.
4. Use data models in pivot tables and charts
Once your data model is ready, you can use it to create powerful pivot tables and charts. The Excel workbook includes a single data model, but you can host as many tables and relationships as you want:
- From Power Pivot, go to 'Manage' and select 'PivotTable'.
- Choose the location of the new pivot table, either on a new or existing sheet.
- When you open the fields panel, you'll see all the tables and fields included in the data model available.
This allows you, for example, to analyze sales by customer, product, and geographic area simultaneously or create dashboards that automatically update when the source data changes.
5. Automate analysis with DAX
DAX (Data Analysis Expressions) is the formula language for Power Pivot and Power BI. With it, you can create custom metrics, automate calculations, and perform advanced analysis without the need for manual formulas spread across thousands of cells. Examples of DAX calculations include KPIs (key performance indicators), growth measures, totals over time, or custom segmentations based on context.
For example, you can automatically calculate total sales by region, average revenue per customer, conversion rates, and much more, simplifying your work and ensuring accurate results.
Easy sharing and collaboration on data models with Power Pivot
Sharing a data model in Excel with Power Pivot is just as easy as sharing with any other Excel file. However, if your company uses collaborative environments such as SharePoint, you can publish your workbooks to servers with Excel Services, allowing other users to analyze and visualize the data directly from their browser, without having to install anything additional.
Furthermore, Power Pivot for SharePoint adds features such as a model gallery, centralized administration, scheduled data updates, and the ability to use your models as a data source for other projects.
Passionate writer about the world of bytes and technology in general. I love sharing my knowledge through writing, and that's what I'll do on this blog, show you all the most interesting things about gadgets, software, hardware, tech trends, and more. My goal is to help you navigate the digital world in a simple and entertaining way.